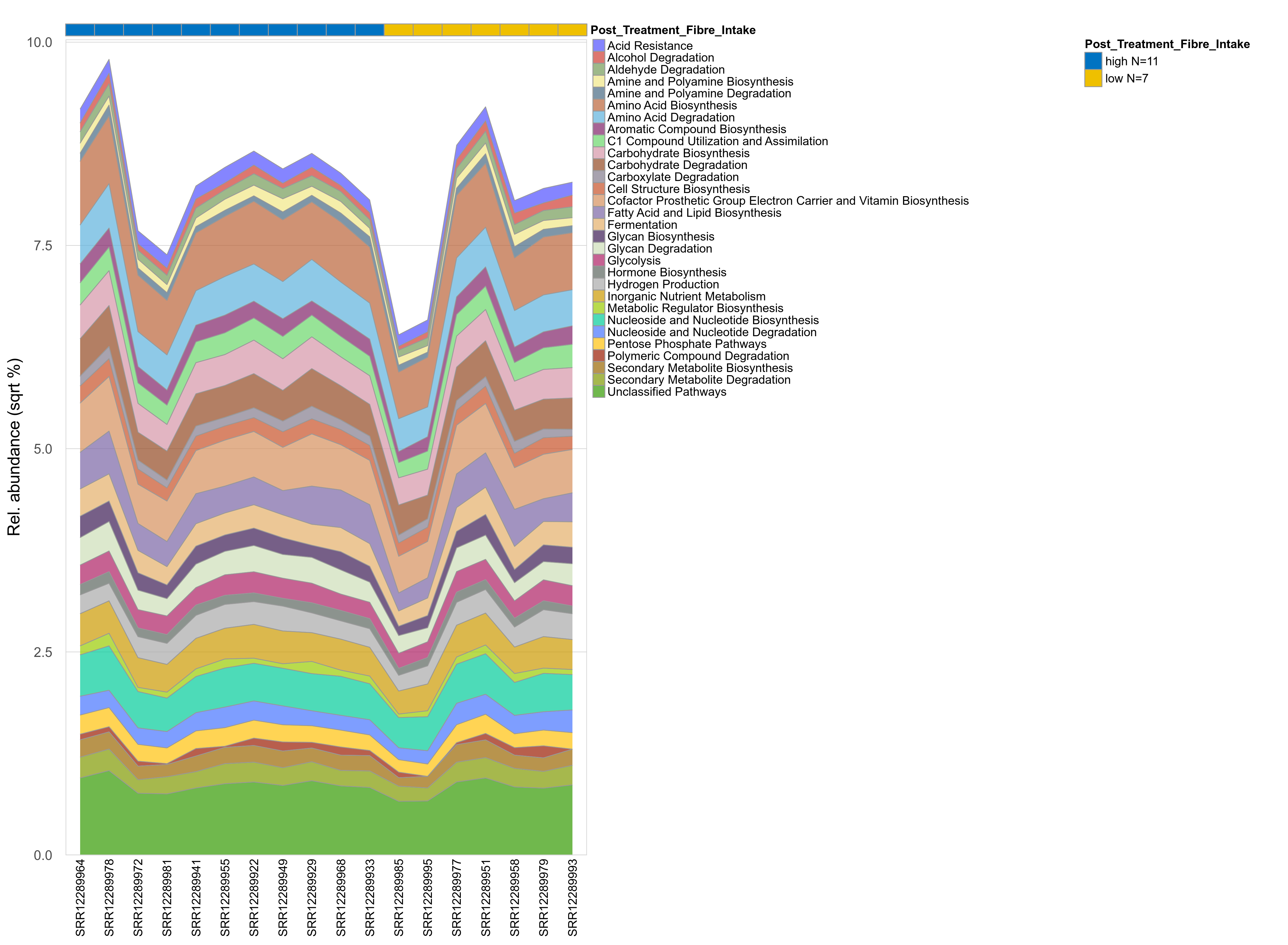
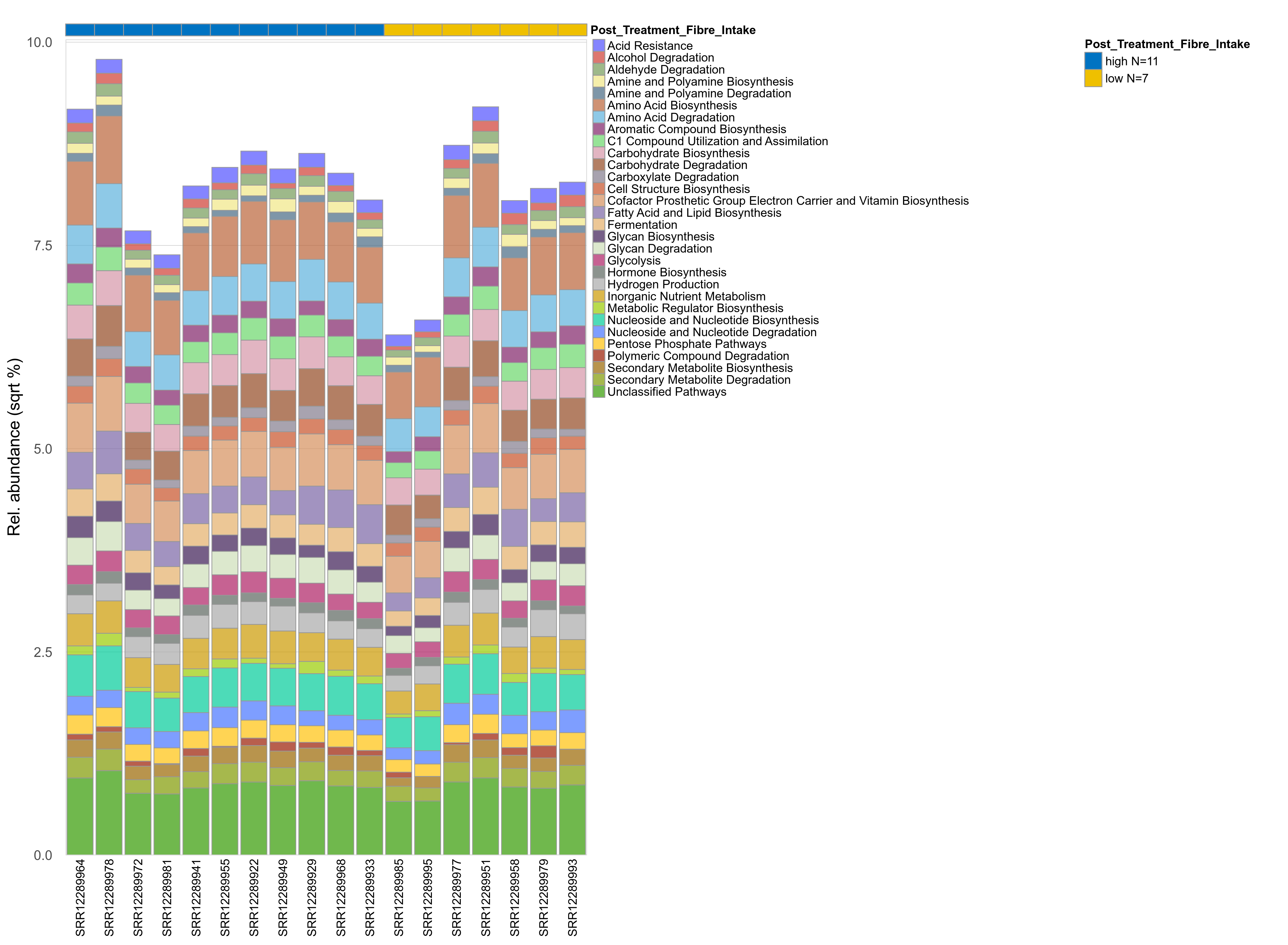
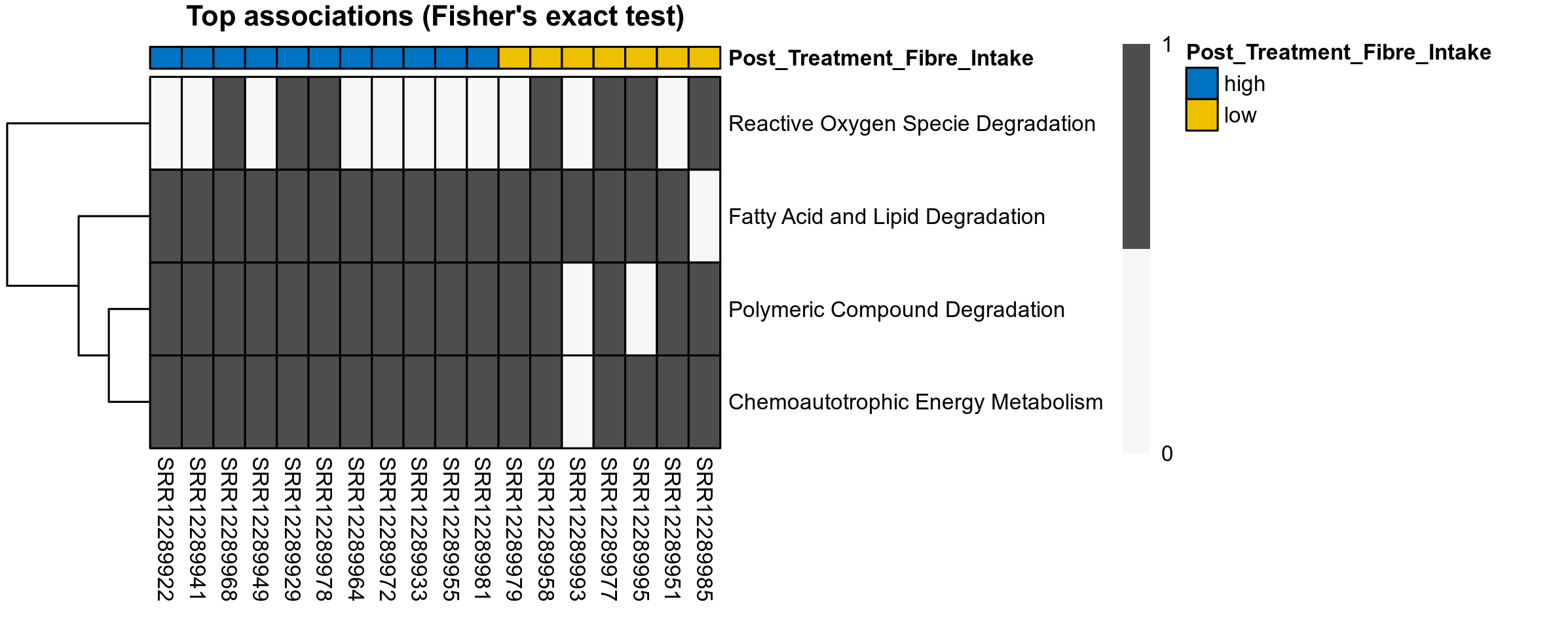
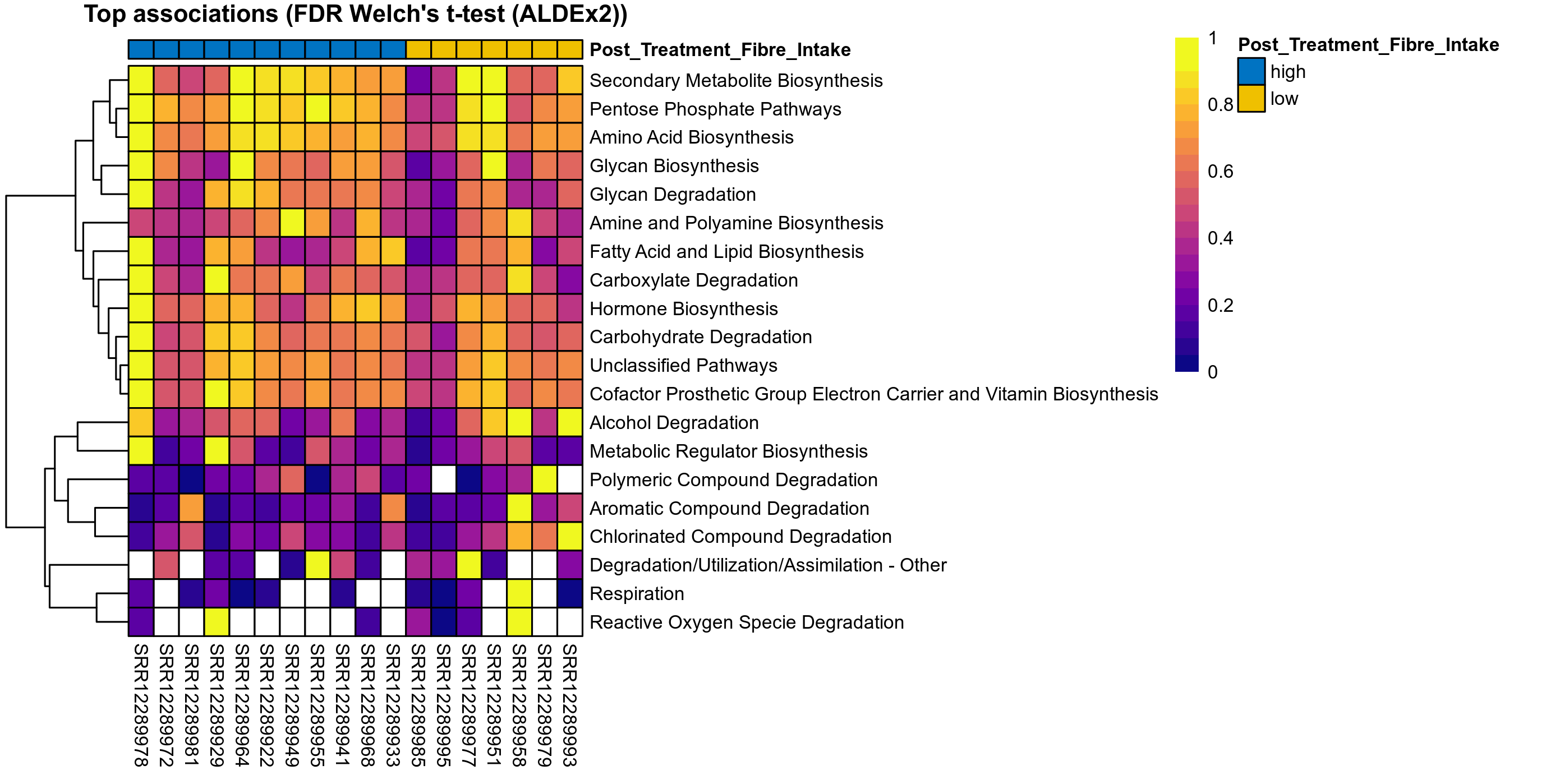
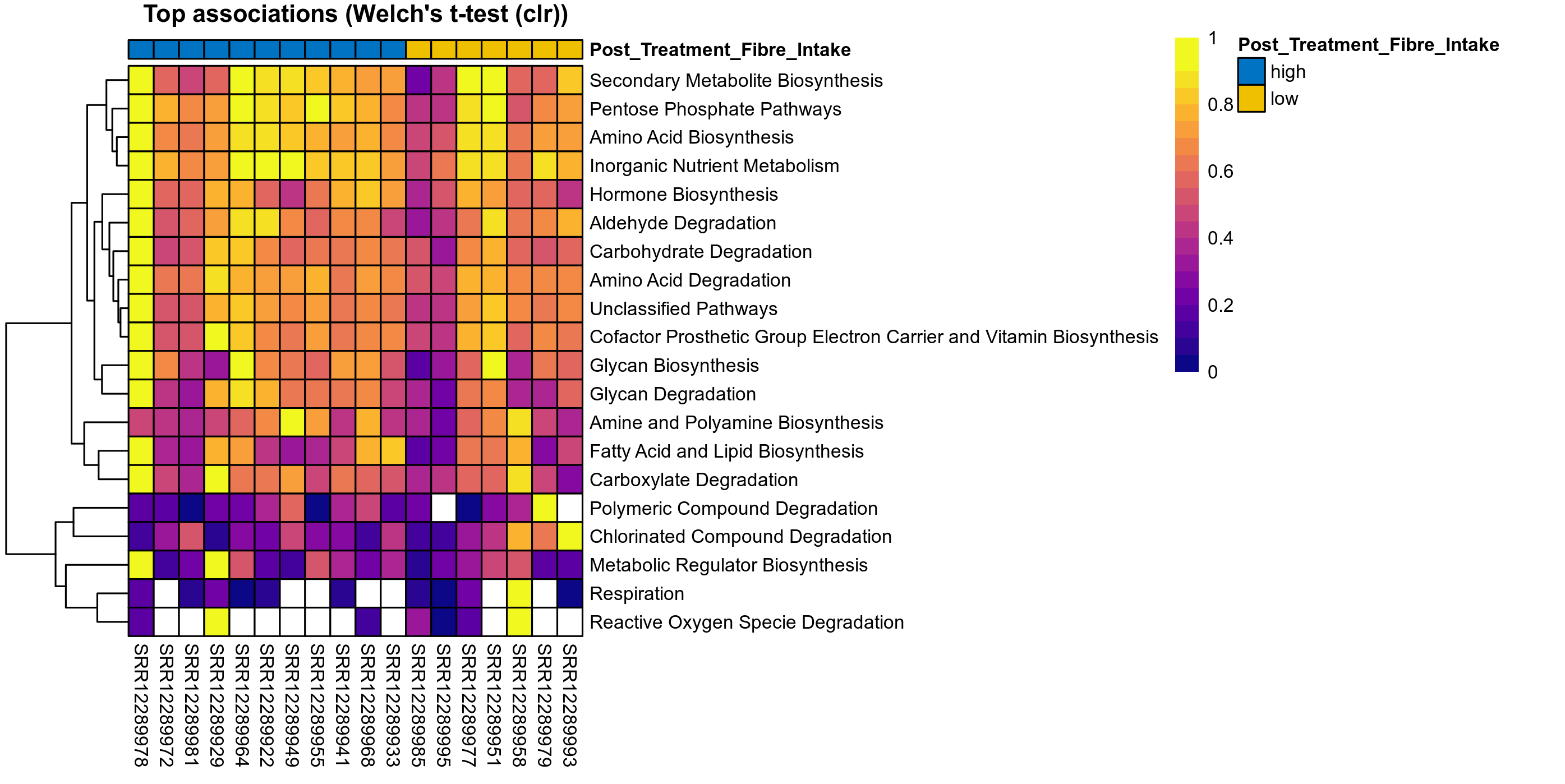
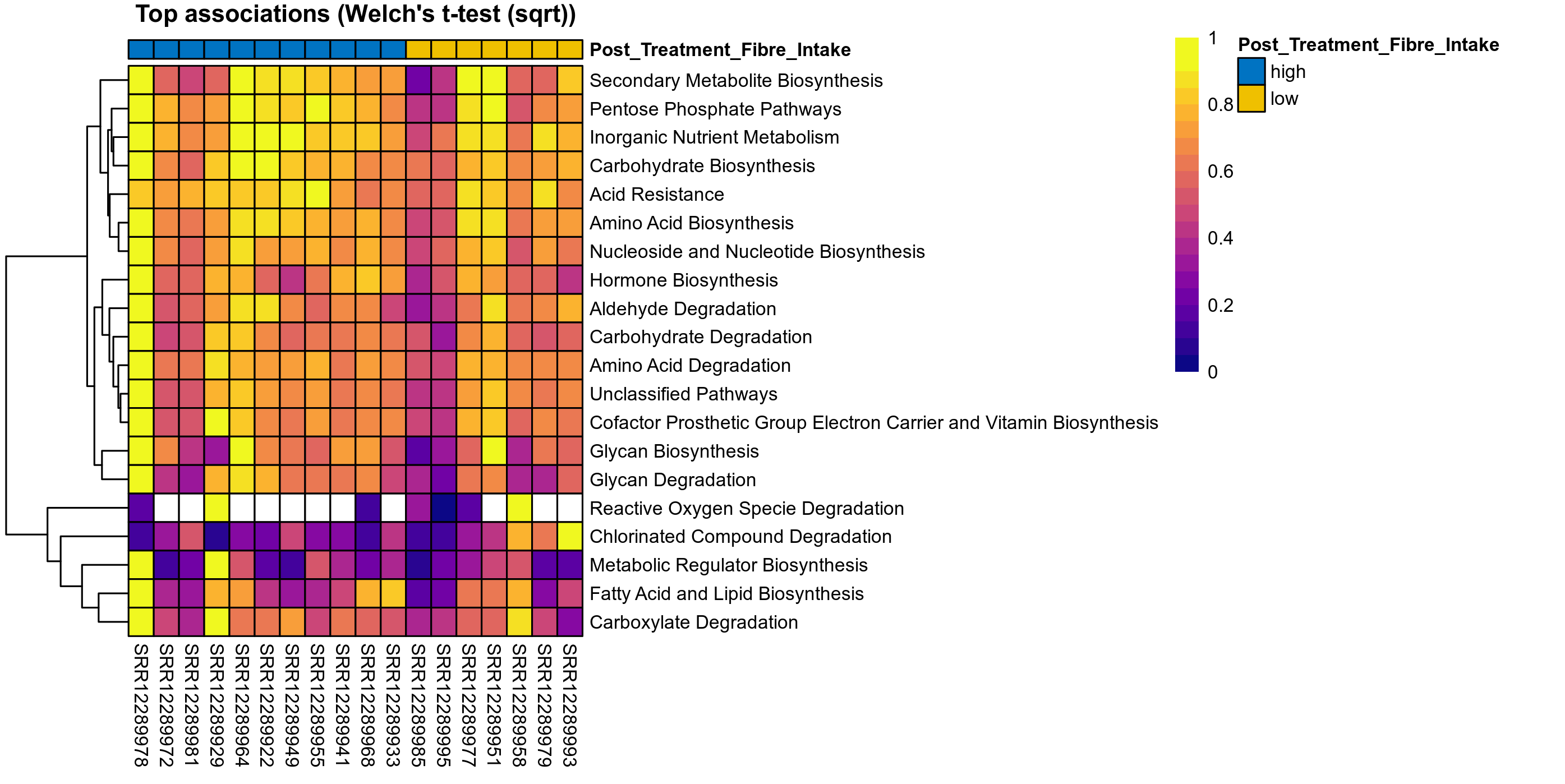
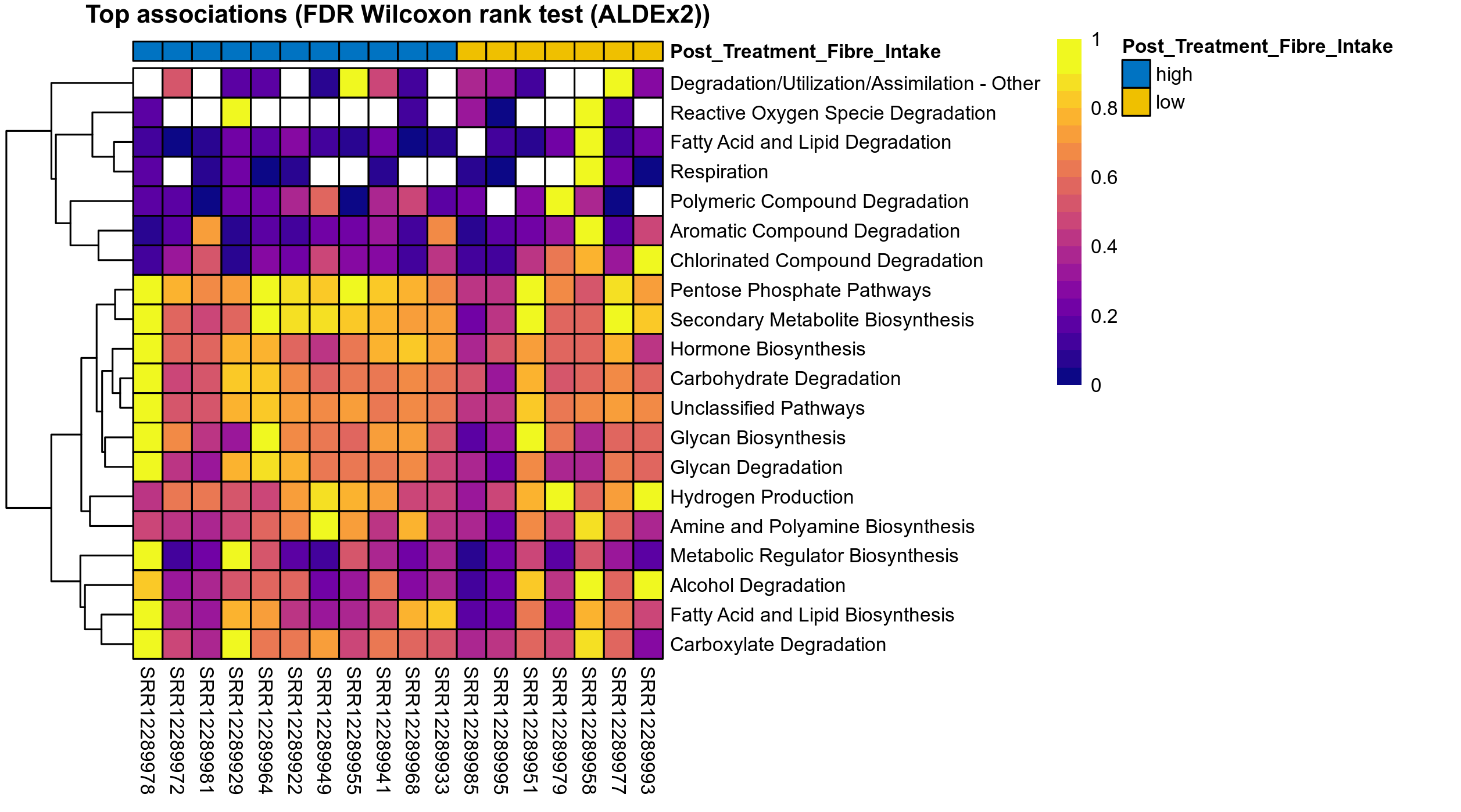
Quantitative visualisation of the top most abundant microbial functions identified in the analysed samples.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
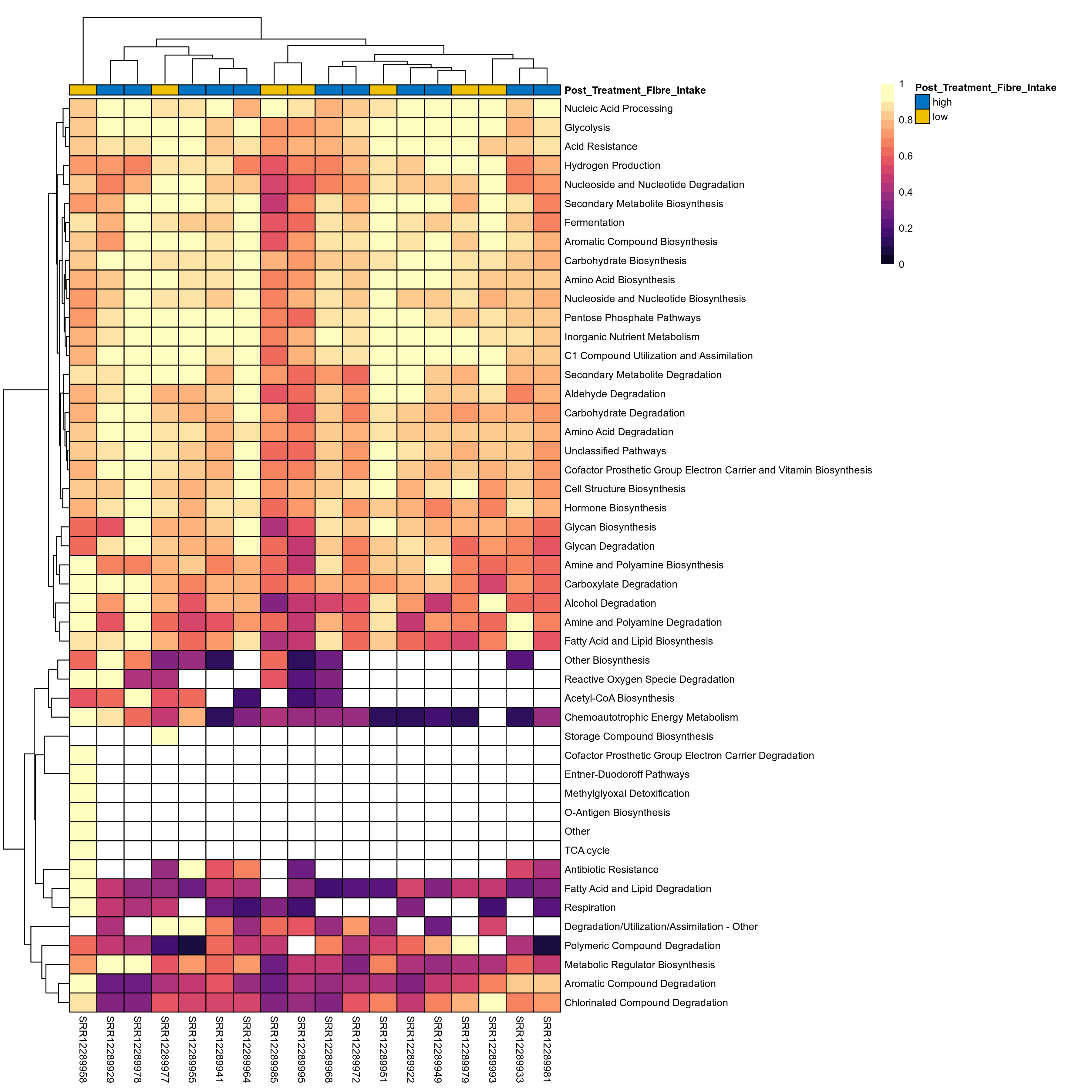
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
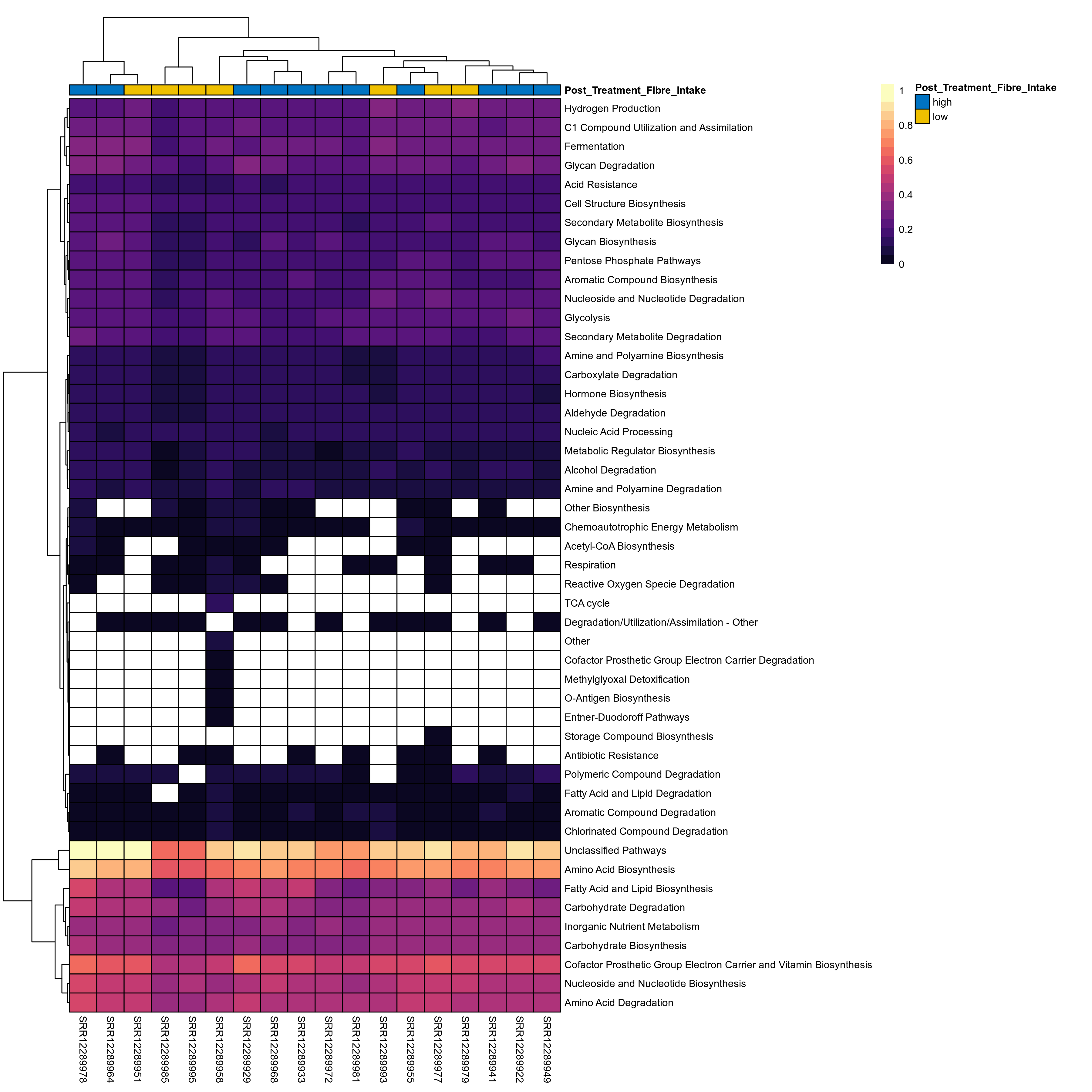
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
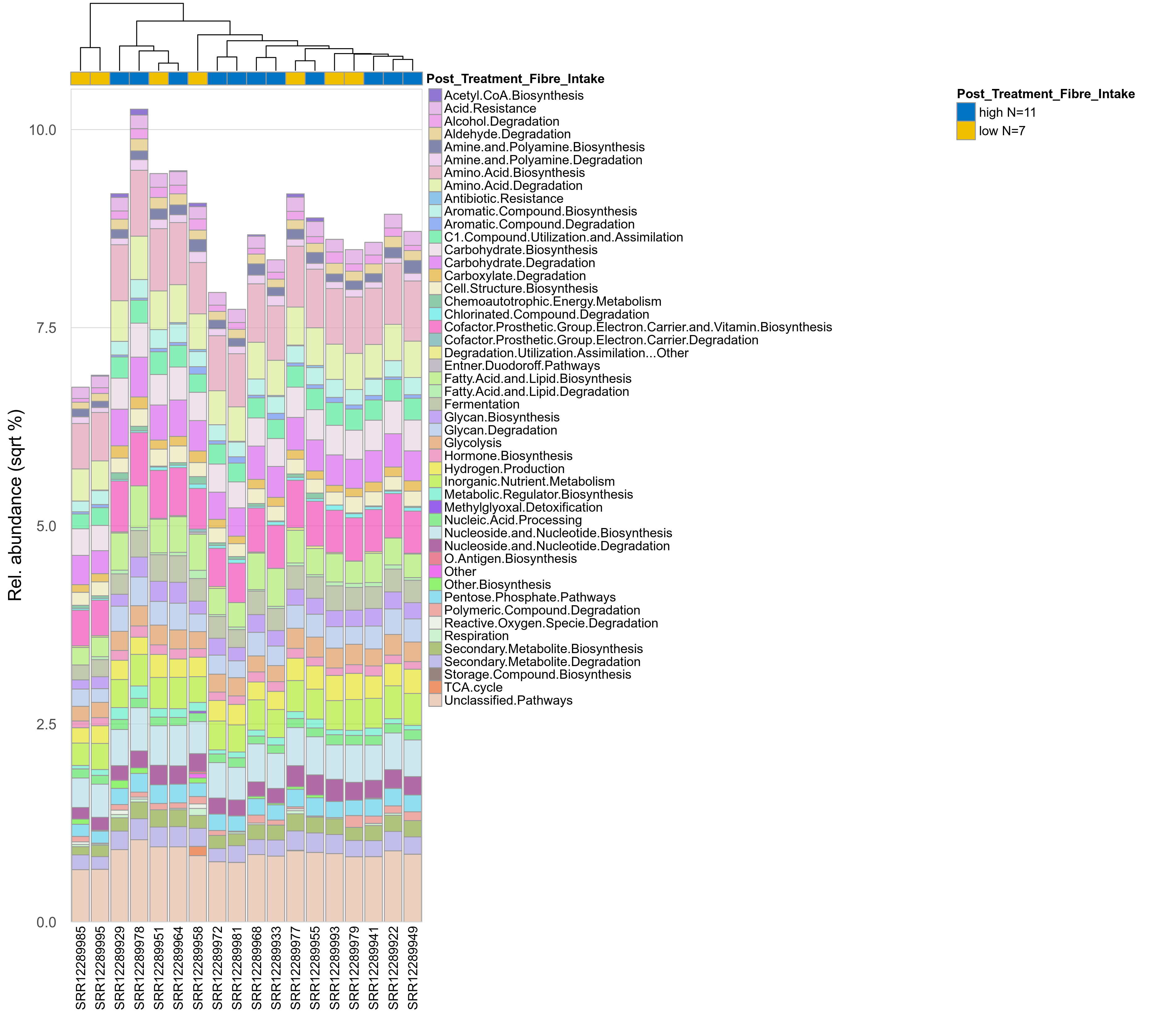
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open interactive barchart in new window.
This page provides an overview of the functional alpha diversity of the analysed sample. Alpha diversity was measured using the Shannon index and functional richnes. Richness measures the total number of gene functions present in each sample. Shannon index combines richness and evenness.
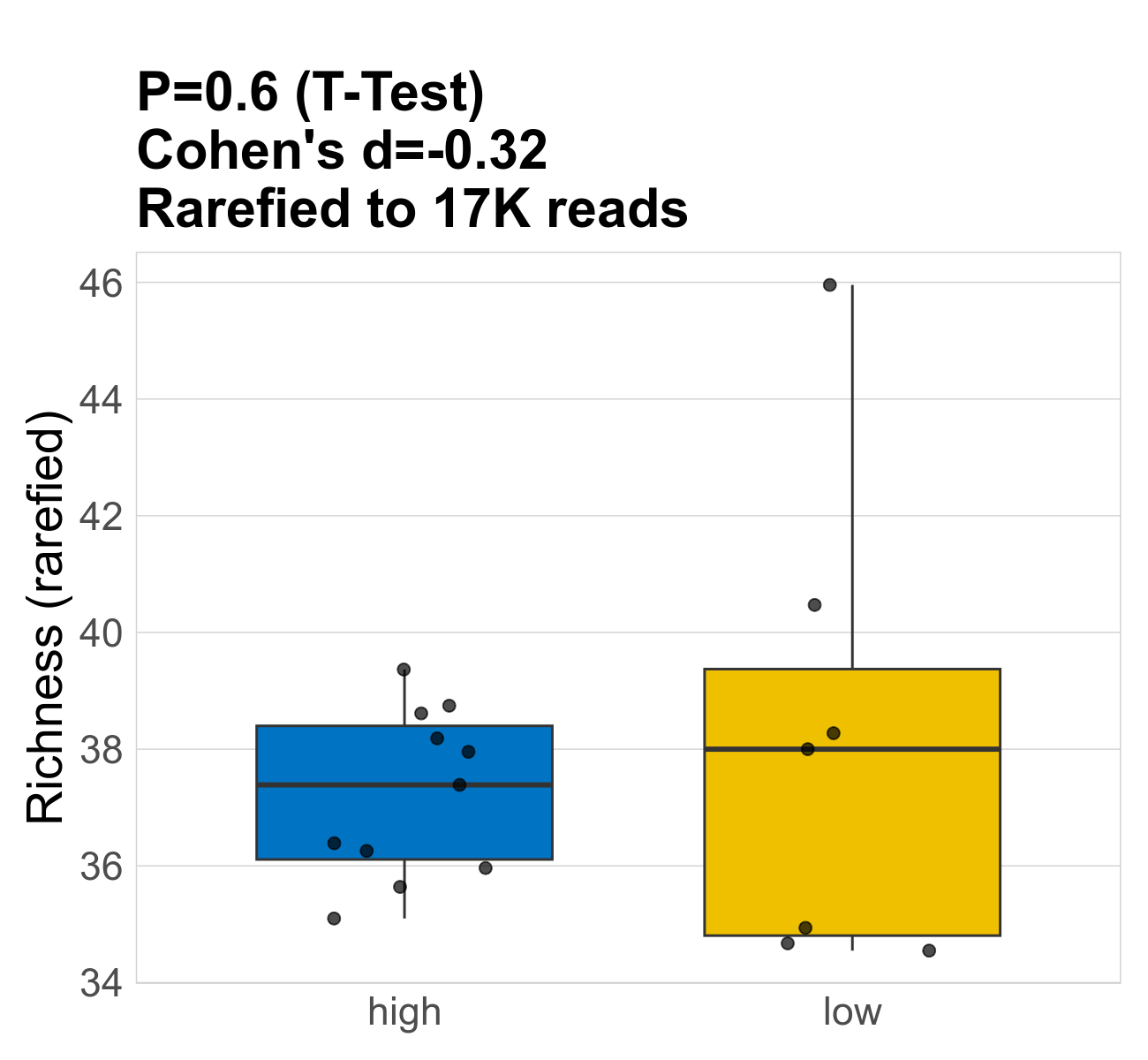
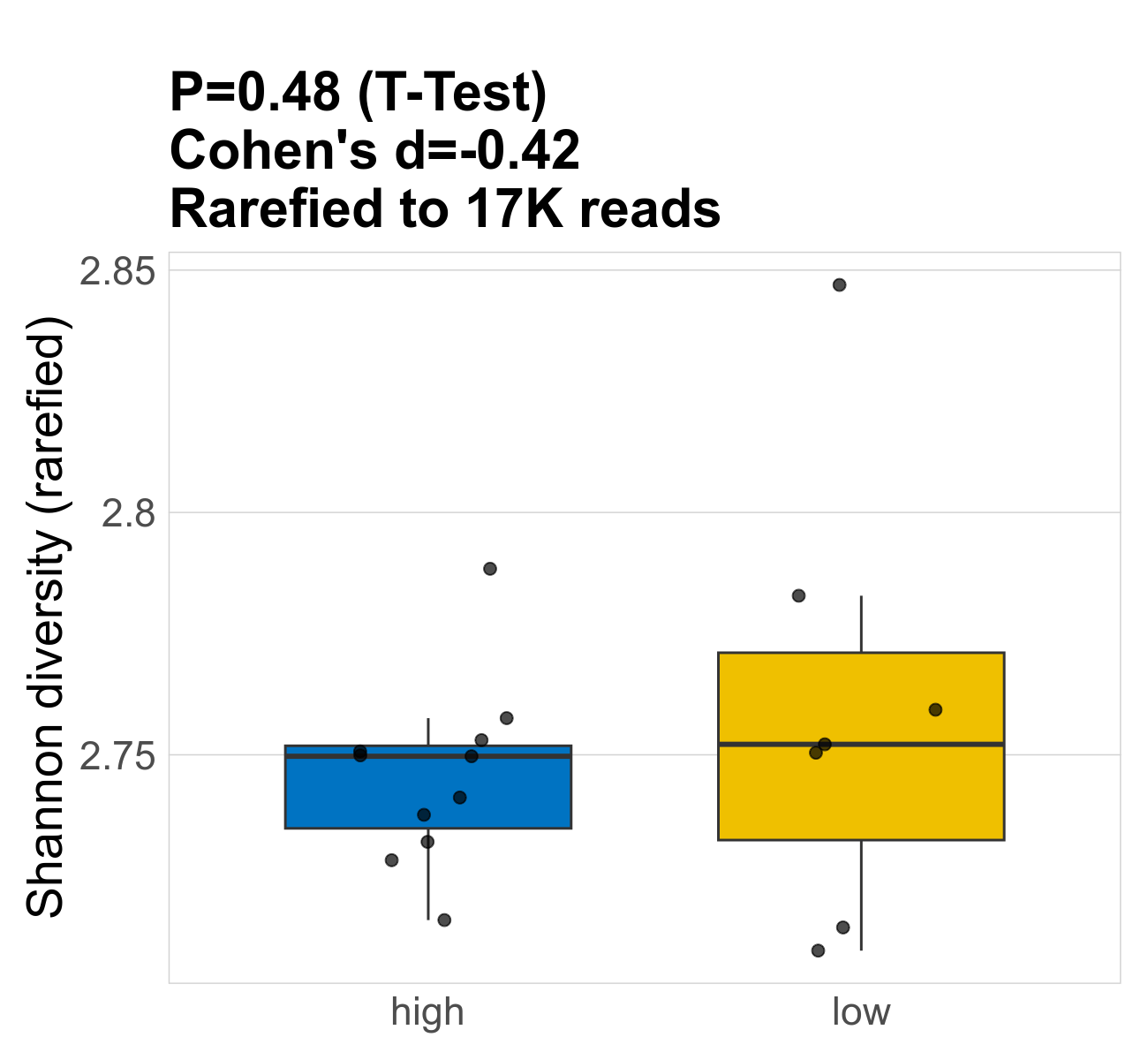
| Index | rarefiedTo | P Welch's t-test | Mean Pos | Mean Abundance | Median Abundance | Mean Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | Median Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | SD Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | Mean Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | Median Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | SD Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | Fold Change Log2(Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow/Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh) | Positive samples | Positive Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | Positive Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | Positive_Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh_percent | Positive_Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow_percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | 16572 | 0.48 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 0.019 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 0.046 | 0.052 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Richness | 16572 | 0.6 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 37 | 37 | 1.4 | 38 | 38 | 4.1 | 0.038 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
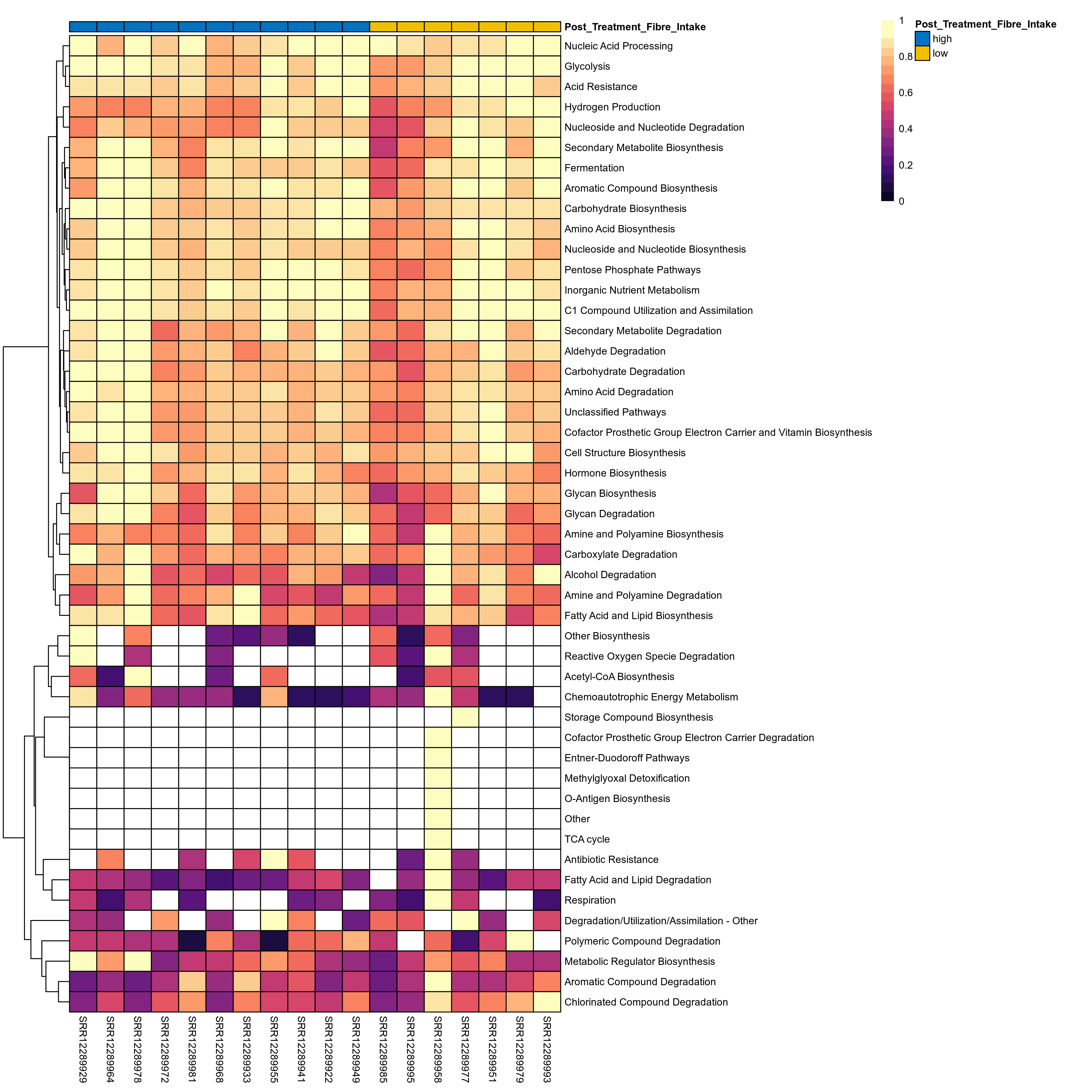
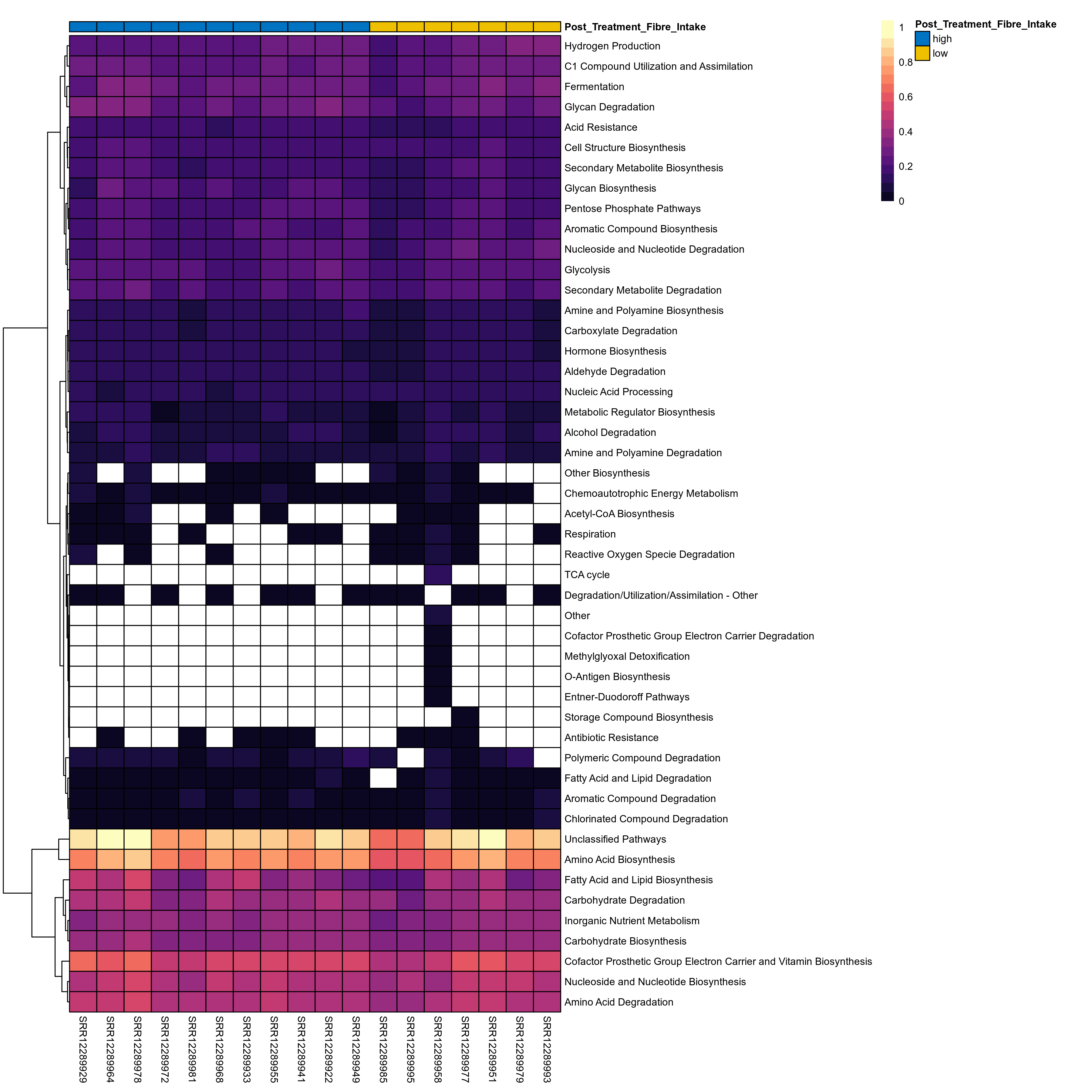
Microbial functions were analyzed using supervised and unsupervised multivariate techniques. Functional profiles were ordinated using the unsupervised methods Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA), Non-Metric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA). The supervised methods Adonis and Redundancy analysis (RDA) were used to assess if variance in the functional profiles was significantly associated with the study condition. A guide explaining these methods can be found here. Sparse Partial Least Square Discriminant Analysis (sPLS-DA) from the MixMc package was additionaly used to extract features associated with the condition of interest.
Differentially abundant microbial functions were identified using the univariate methods ANOVA or LMER (linear mixed effect regression) on clr transformed relative abundance data, Fisher's exact test, and Aldex2 (ANOVA-like Differential Expression). Aldex2 was run on read count data. Fisher's exact test was used to test for diffrerences in the presence and absence (detection rate) of microbial functions across study groups.
LMER is used for repeated measures data, using random effects to control for correlation between samples from the same subject. Fixed effects are included for treatment groups, time, and treatment over time, where appropriate. The LMER P values correspond to a nested model test of the significance of including the corresponding fixed effect.
ALDEx2 uses subsampling (Bayesian sampling) to estimate the underlying technical variation. For each subsample instance, center log-ratio transformed data is statistically compared across study groups and computed P values are corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure. The expected P value (mean P value) is reported, which are those that would likely have been observed if the same samples had been run multiple times. The expected values are reported for both the distribution of P values and for the distribution of Benjamini–Hochberg corrected values.
| Function | P Welch's t-test (sqrt) | FDR Welch's t-test (sqrt) | Pbonf Welch's t-test (sqrt) | Cohen's d Welch's t-test (sqrt) | P Welch's t-test (clr) | FDR Welch's t-test (clr) | Pbonf Welch's t-test (clr) | Cohen's d Welch's t-test (clr) | P Fisher's exact test | FDR Fisher's exact test | Pbonf Fisher's exact test | P Welch's t-test (ALDEx2) | FDR Welch's t-test (ALDEx2) | P Wilcoxon rank test (ALDEx2) | FDR Wilcoxon rank test (ALDEx2) | Mean Pos | Mean Abundance | Median Abundance | Mean Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | Median Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | SD Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | Mean Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | Median Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | SD Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | Fold Change Log2(Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow/Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh) | Positive samples | Positive Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh | Positive Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow | Positive_Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakehigh_percent | Positive_Post_Treatment_Fibre_Intakelow_percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | 0.74 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.18 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 1 | 0.17 | NA | NA | NA | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 0.98 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.058 | 0.055 | 0.058 | 0.0095 | 0.053 | 0.062 | 0.014 | -0.053 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
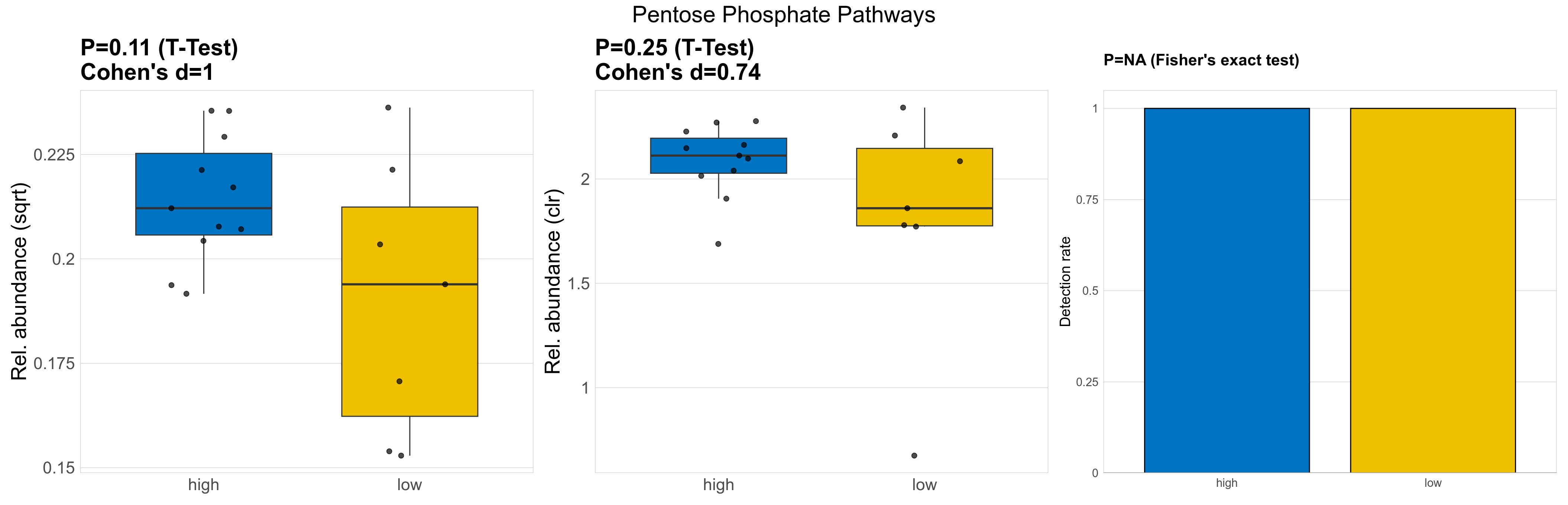
| Pentose Phosphate Pathways | 0.11 | 0.74 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.74 | NA | NA | NA | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.36 | 0.96 | 0.043 | 0.043 | 0.043 | 0.046 | 0.045 | 0.0065 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.013 | -0.31 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Alcohol Degradation | 0.5 | 0.83 | 1 | -0.39 | 0.7 | 0.93 | 1 | -0.22 | NA | NA | NA | 0.55 | 0.93 | 0.52 | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0097 | 0.0092 | 0.0076 | 0.0037 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.0072 | 0.38 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Cell Structure Biosynthesis | 0.74 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 1 | 0.14 | NA | NA | NA | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.73 | 0.98 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.0064 | 0.034 | 0.032 | 0.0073 | -0.042 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Aromatic Compound Degradation | 0.57 | 0.85 | 1 | -0.29 | 0.53 | 0.9 | 1 | -0.28 | NA | NA | NA | 0.5 | 0.92 | 0.61 | 0.98 | 0.0026 | 0.0026 | 0.0018 | 0.0024 | 0.0018 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.0018 | 0.0028 | 0.32 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Fermentation | 0.68 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.23 | 0.61 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.3 | NA | NA | NA | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.081 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.018 | 0.078 | 0.083 | 0.027 | -0.072 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
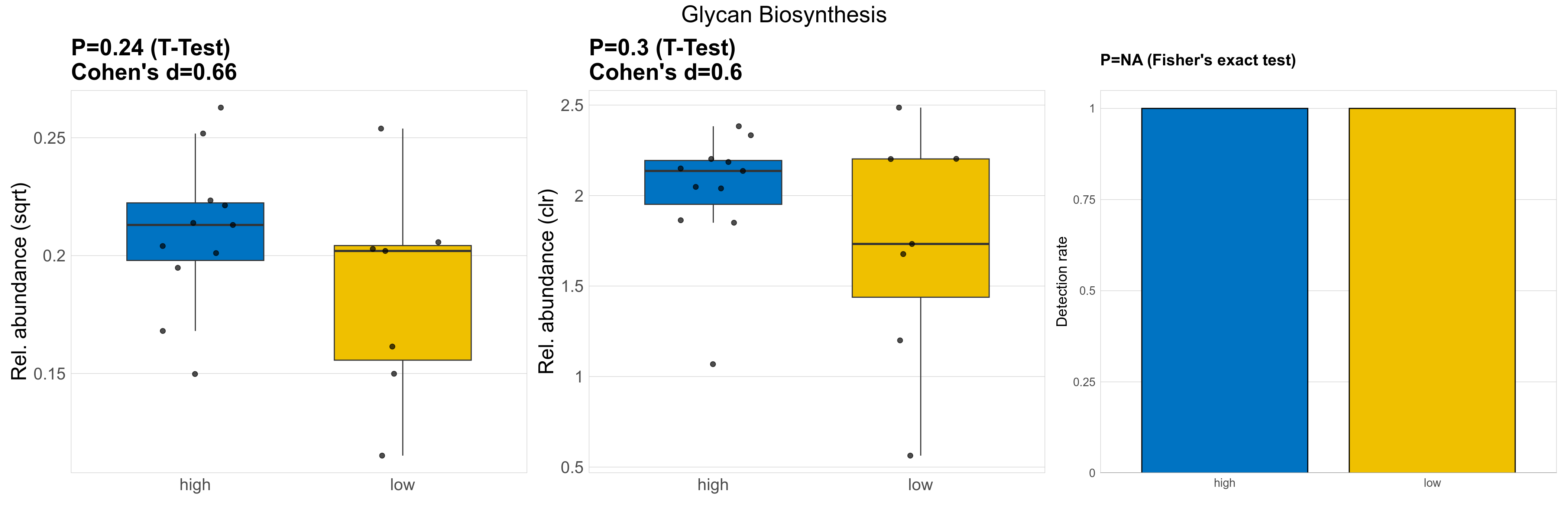
| Glycan Biosynthesis | 0.24 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.6 | NA | NA | NA | 0.38 | 0.9 | 0.48 | 0.97 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.014 | 0.036 | 0.041 | 0.017 | -0.32 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
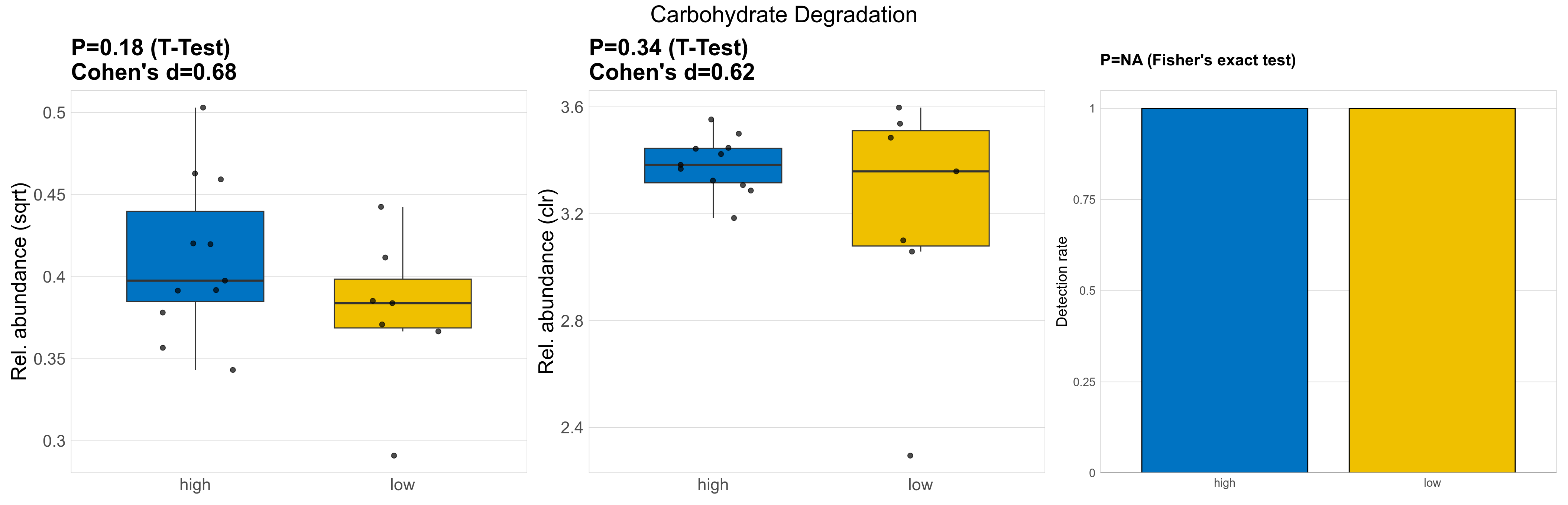
| Carbohydrate Degradation | 0.18 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.68 | 0.34 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.62 | NA | NA | NA | 0.46 | 0.9 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.041 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.034 | -0.18 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Hydrogen Production | 0.58 | 0.85 | 1 | -0.31 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 1 | -0.13 | NA | NA | NA | 0.6 | 0.94 | 0.63 | 0.98 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 0.074 | 0.079 | 0.026 | 0.14 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
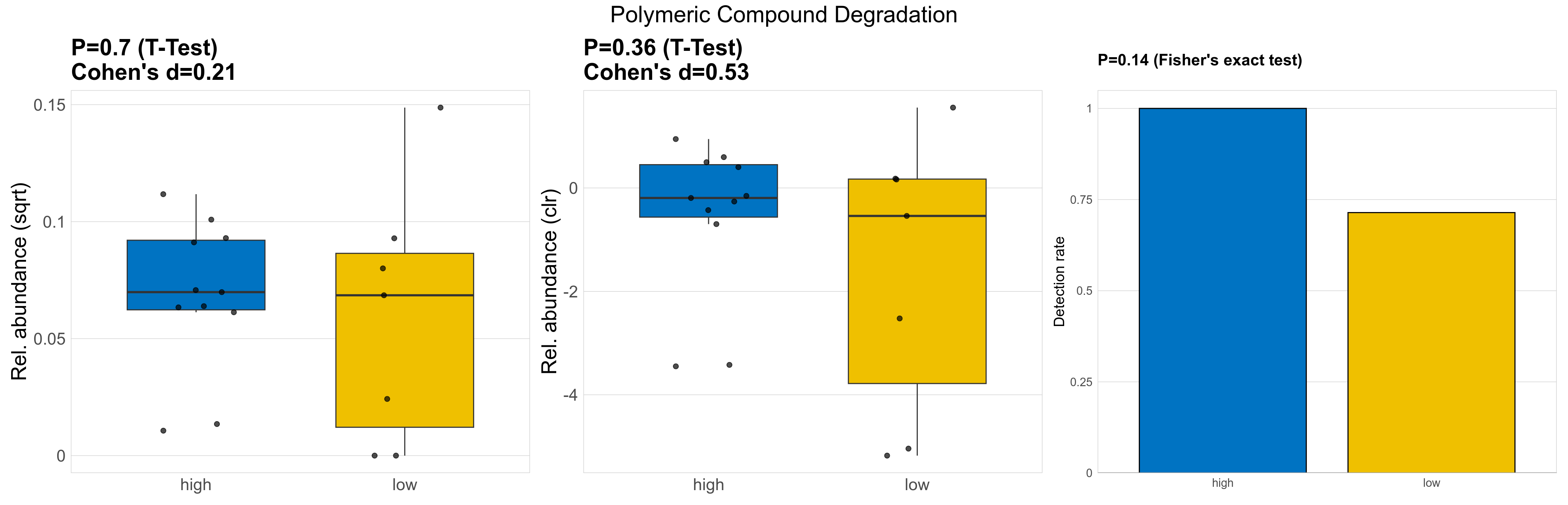
| Polymeric Compound Degradation | 0.7 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 0.87 | 1 | 0.36 | 0.9 | 0.66 | 0.98 | 0.0065 | 0.0058 | 0.0048 | 0.0056 | 0.0049 | 0.0039 | 0.0061 | 0.0047 | 0.0079 | 0.12 | 16 / 18 (89%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 5 / 7 (71%) | 1 | 0.714 |
| Aldehyde Degradation | 0.4 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.45 | NA | NA | NA | 0.62 | 0.91 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.015 | 0.0037 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.0046 | -0.19 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
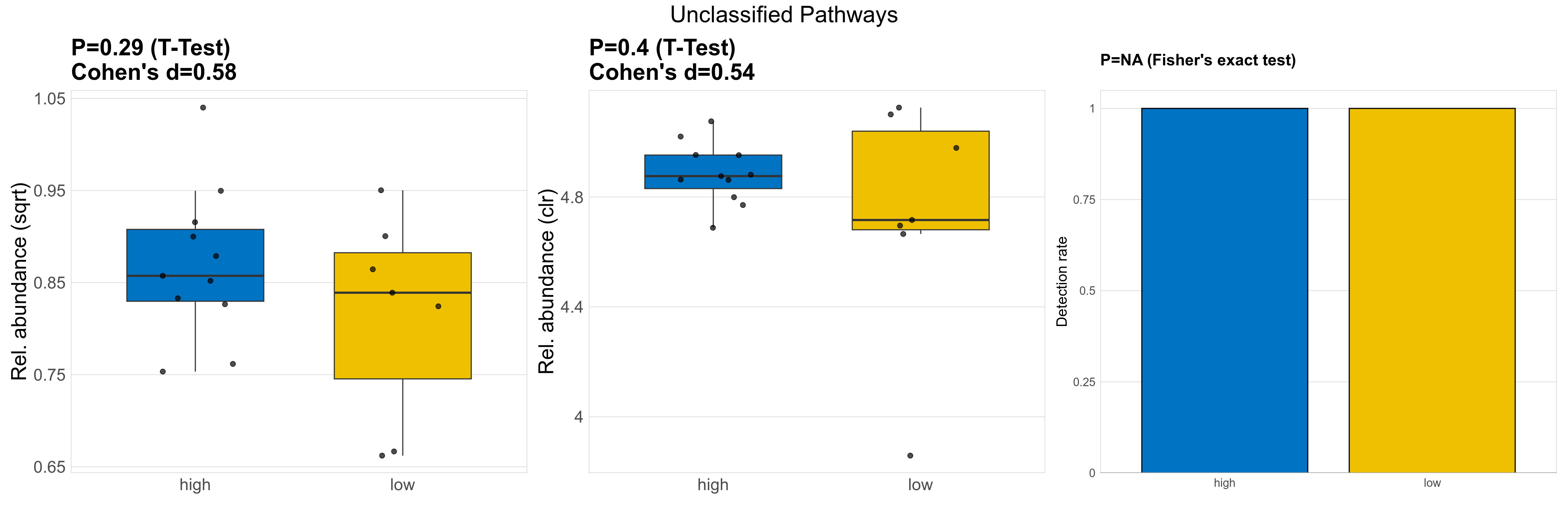
| Unclassified Pathways | 0.29 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.54 | NA | NA | NA | 0.56 | 0.9 | 0.65 | 0.97 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.15 | 0.68 | 0.7 | 0.18 | -0.16 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
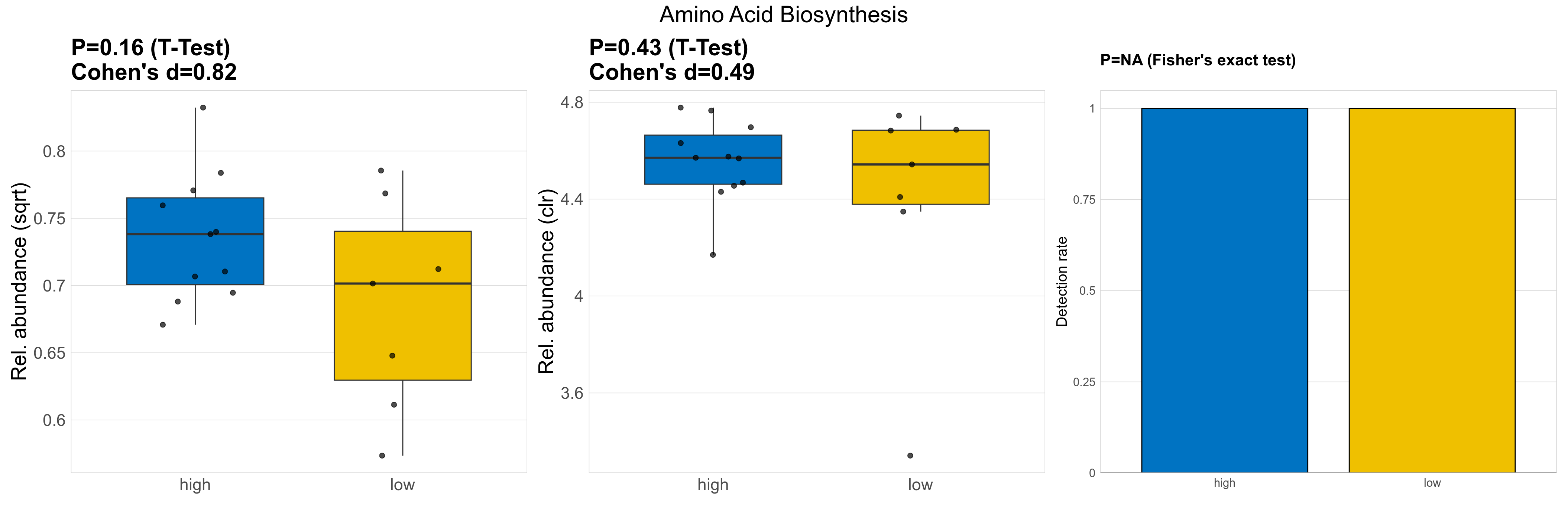
| Amino Acid Biosynthesis | 0.16 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.82 | 0.43 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.49 | NA | NA | NA | 0.57 | 0.9 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.072 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.11 | -0.17 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Amine and Polyamine Degradation | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1 | -0.027 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 1 | 0.028 | NA | NA | NA | 0.76 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 0.0095 | 0.0095 | 0.0083 | 0.0094 | 0.0088 | 0.0043 | 0.0097 | 0.0078 | 0.005 | 0.045 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
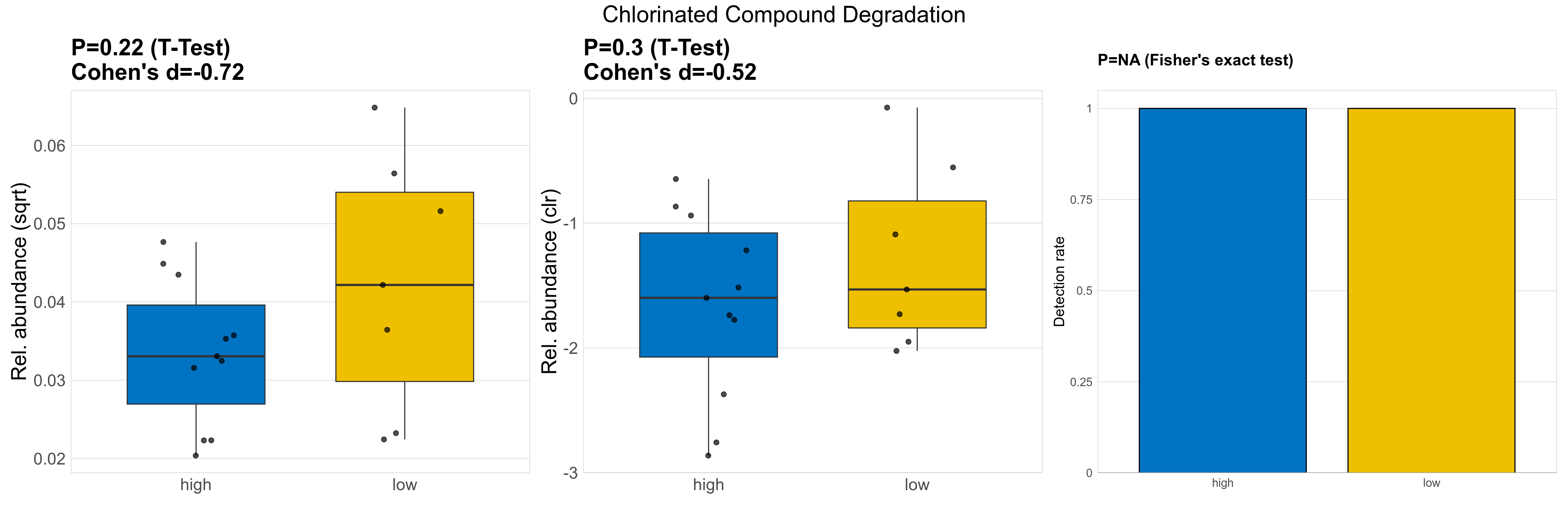
| Chlorinated Compound Degradation | 0.22 | 0.74 | 1 | -0.72 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1 | -0.52 | NA | NA | NA | 0.29 | 0.9 | 0.41 | 0.97 | 0.0015 | 0.0015 | 0.0013 | 0.0012 | 0.0011 | 0.00063 | 0.002 | 0.0018 | 0.0014 | 0.74 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Acetyl-CoA Biosynthesis | 0.73 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 1 | 0.11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 0.72 | 0.98 | 0.0018 | 8e-04 | 0 | 0.00095 | 0 | 0.0018 | 0.00057 | 0 | 0.00091 | -0.74 | 8 / 18 (44%) | 5 / 11 (45%) | 3 / 7 (43%) | 0.455 | 0.429 |
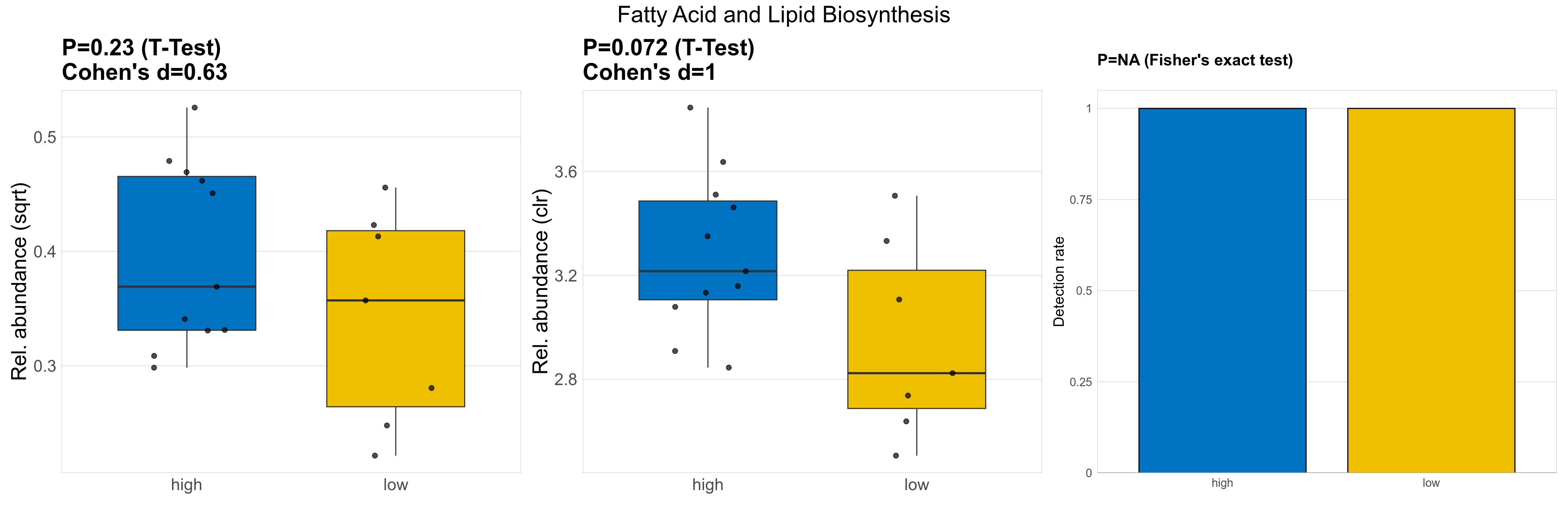
| Fatty Acid and Lipid Biosynthesis | 0.23 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.63 | 0.072 | 0.9 | 1 | 1 | NA | NA | NA | 0.14 | 0.89 | 0.16 | 0.95 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.066 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.063 | -0.42 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Other Biosynthesis | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1 | -0.0091 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 1 | -0.047 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.0028 | 0.0015 | 0.00011 | 0.0016 | 0.00011 | 0.0032 | 0.0014 | 0.00011 | 0.002 | -0.19 | 10 / 18 (56%) | 6 / 11 (55%) | 4 / 7 (57%) | 0.545 | 0.571 |
| Acid Resistance | 0.34 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.28 | NA | NA | NA | 0.75 | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.98 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.0037 | 0.026 | 0.025 | 0.0048 | -0.11 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
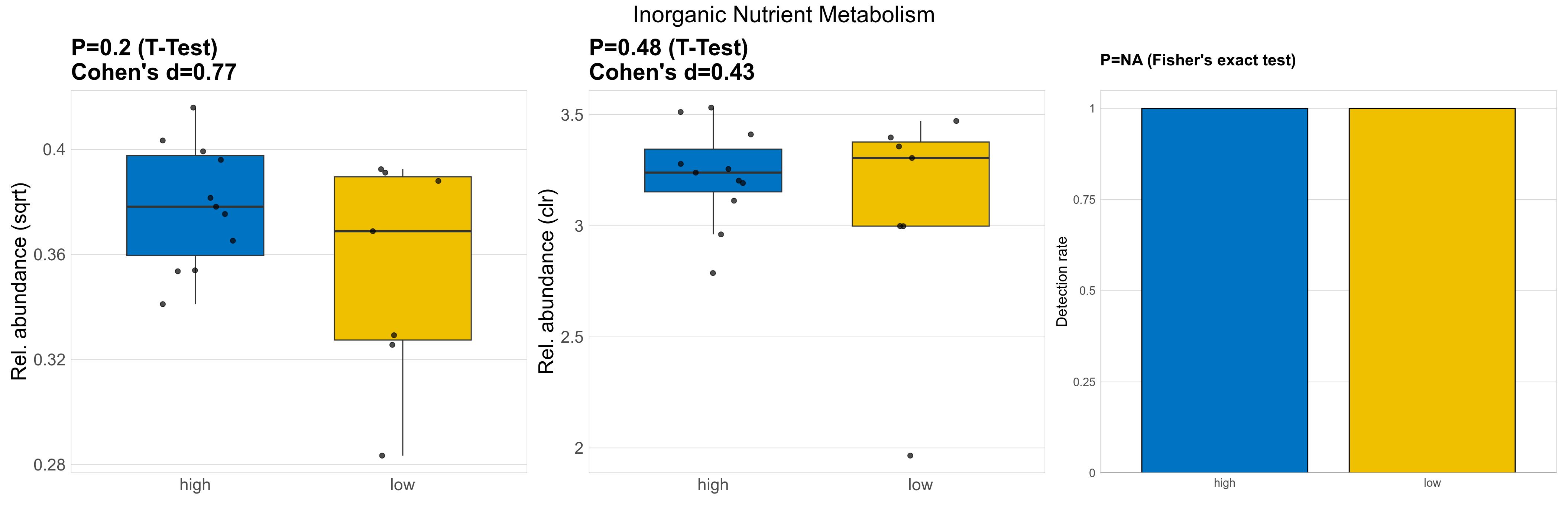
| Inorganic Nutrient Metabolism | 0.2 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.77 | 0.48 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.43 | NA | NA | NA | 0.63 | 0.9 | 0.78 | 0.97 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.018 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.029 | -0.11 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
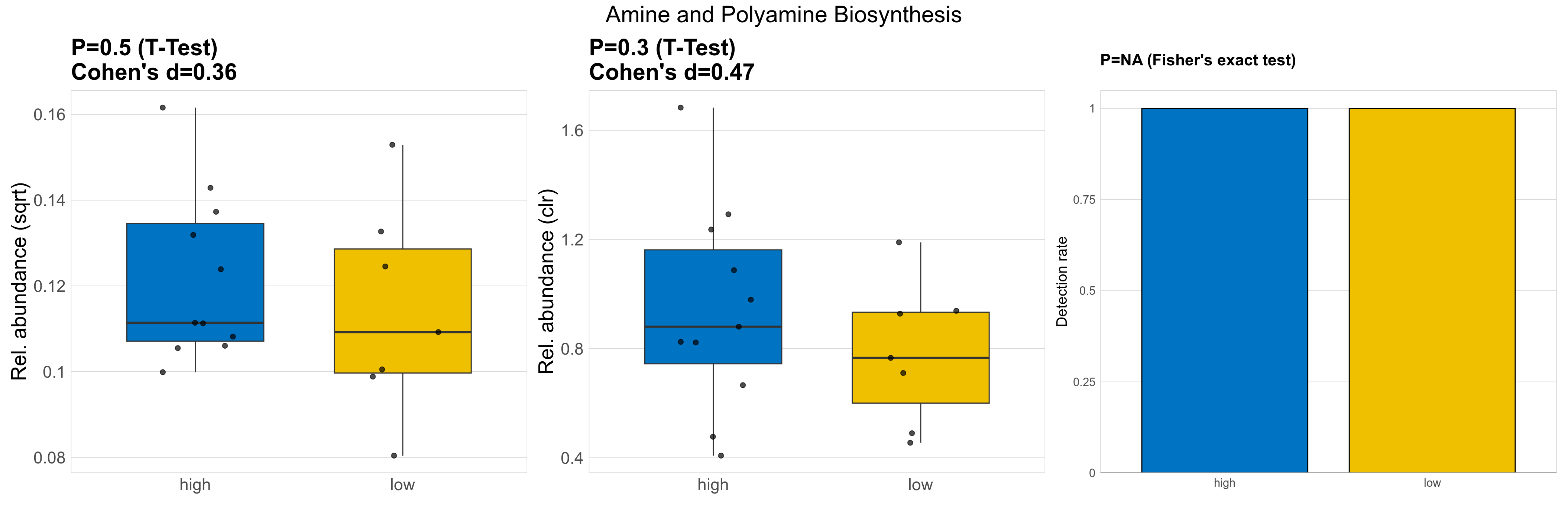
| Amine and Polyamine Biosynthesis | 0.5 | 0.83 | 1 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.47 | NA | NA | NA | 0.58 | 0.9 | 0.66 | 0.97 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.005 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.0057 | -0.1 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Secondary Metabolite Degradation | 0.75 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 1 | 0.2 | NA | NA | NA | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.049 | 0.049 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.048 | 0.013 | 0.048 | 0.052 | 0.014 | -0.059 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Aromatic Compound Biosynthesis | 0.44 | 0.79 | 1 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.39 | NA | NA | NA | 0.68 | 0.91 | 0.78 | 0.97 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.044 | 0.042 | 0.0075 | 0.04 | 0.038 | 0.013 | -0.14 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
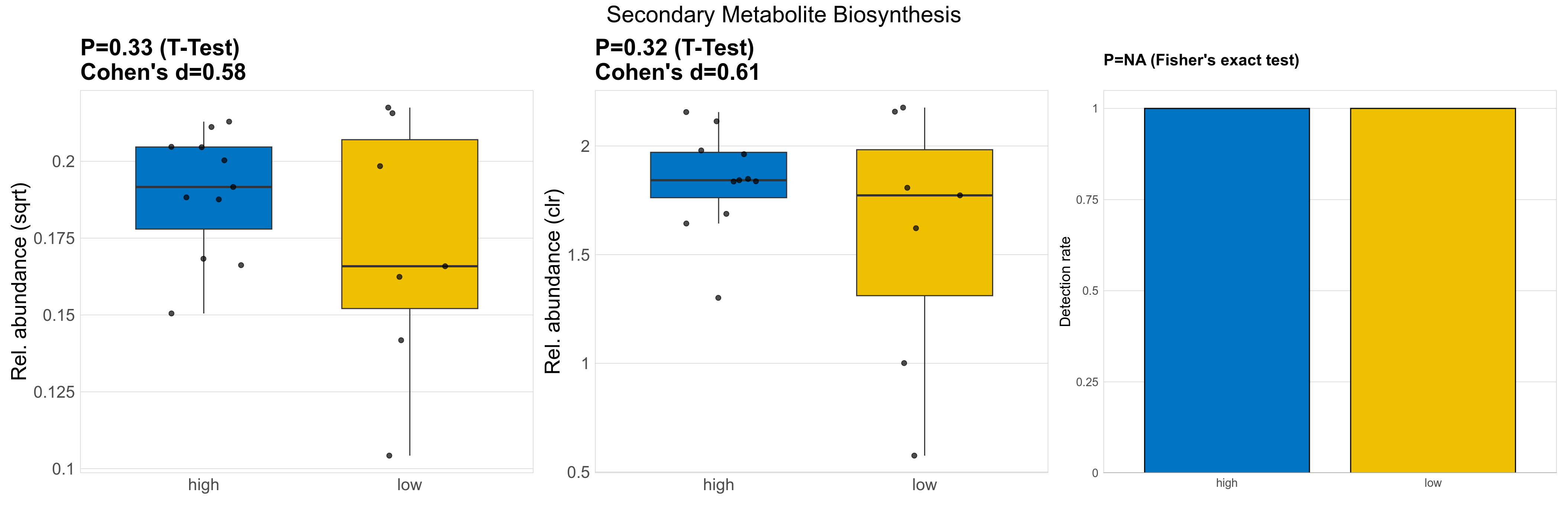
| Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis | 0.33 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.32 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.61 | NA | NA | NA | 0.42 | 0.9 | 0.54 | 0.97 | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.037 | 0.0074 | 0.031 | 0.028 | 0.014 | -0.22 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
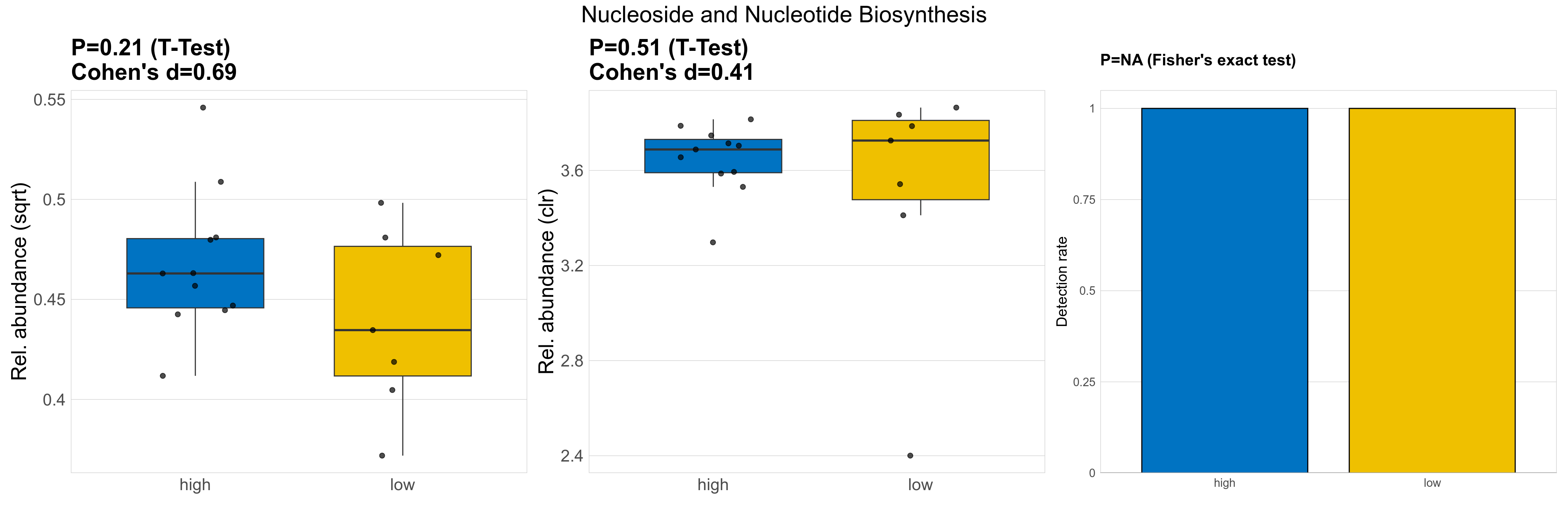
| Nucleoside and Nucleotide Biosynthesis | 0.21 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.41 | NA | NA | NA | 0.67 | 0.9 | 0.78 | 0.97 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.035 | 0.2 | 0.19 | 0.04 | -0.14 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Antibiotic Resistance | 0.78 | 0.86 | 1 | 0.14 | 0.64 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.21 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.62 | 0.92 | 0.7 | 0.98 | 3e-04 | 0.00013 | 0 | 0.00014 | 0 | 0.00021 | 0.00012 | 0 | 0.00026 | -0.22 | 8 / 18 (44%) | 5 / 11 (45%) | 3 / 7 (43%) | 0.455 | 0.429 |
| Chemoautotrophic Energy Metabolism | 0.84 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 0.002 | 0.0019 | 0.0011 | 0.0018 | 0.0011 | 0.0023 | 0.0019 | 0.0011 | 0.0031 | 0.078 | 17 / 18 (94%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 6 / 7 (86%) | 1 | 0.857 |
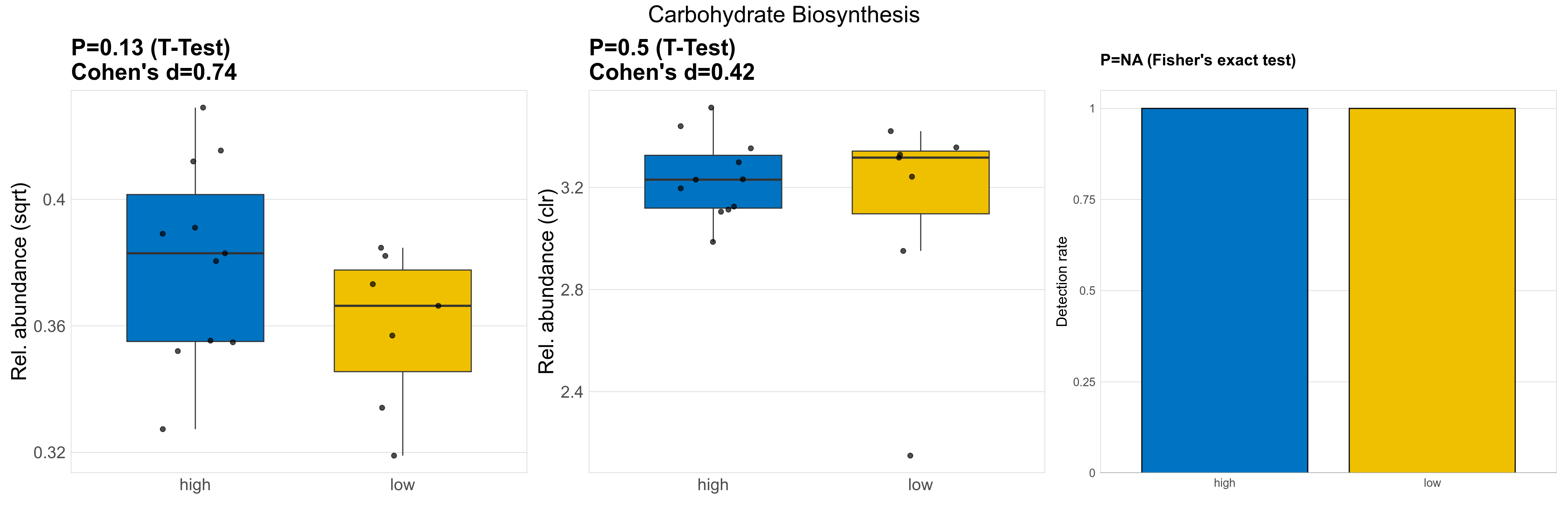
| Carbohydrate Biosynthesis | 0.13 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.74 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.42 | NA | NA | NA | 0.68 | 0.9 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.024 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.017 | -0.21 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
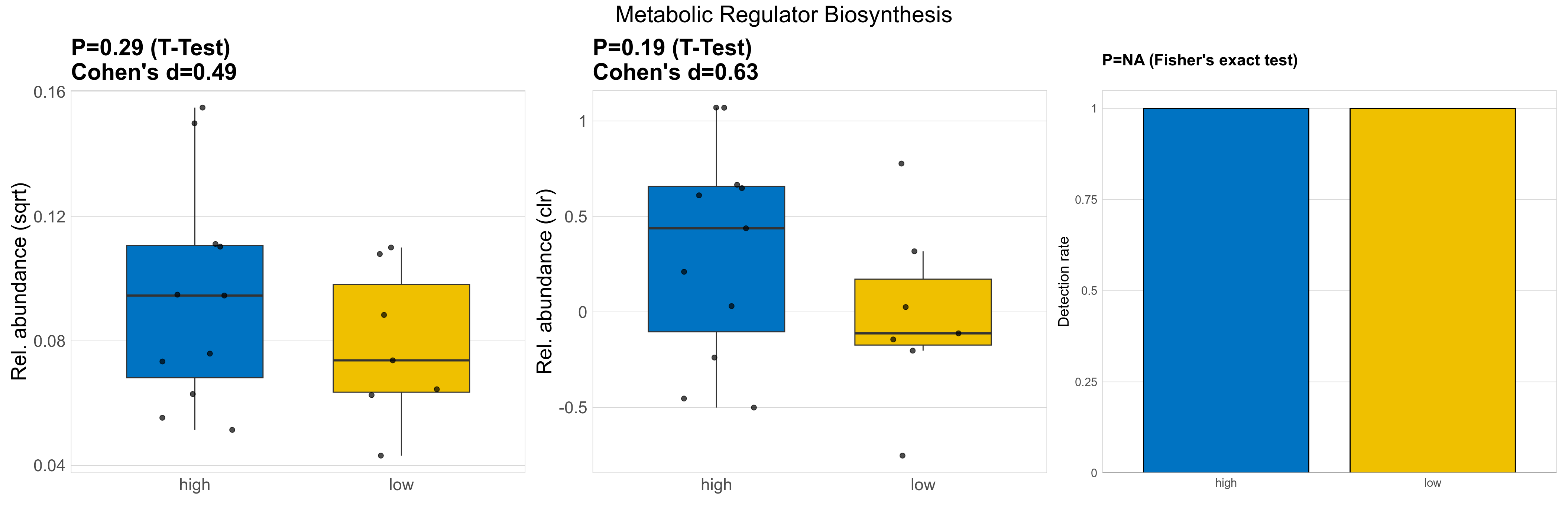
| Metabolic Regulator Biosynthesis | 0.29 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.63 | NA | NA | NA | 0.31 | 0.9 | 0.35 | 0.96 | 0.0087 | 0.0087 | 0.0068 | 0.01 | 0.0089 | 0.0074 | 0.0067 | 0.0054 | 0.004 | -0.58 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
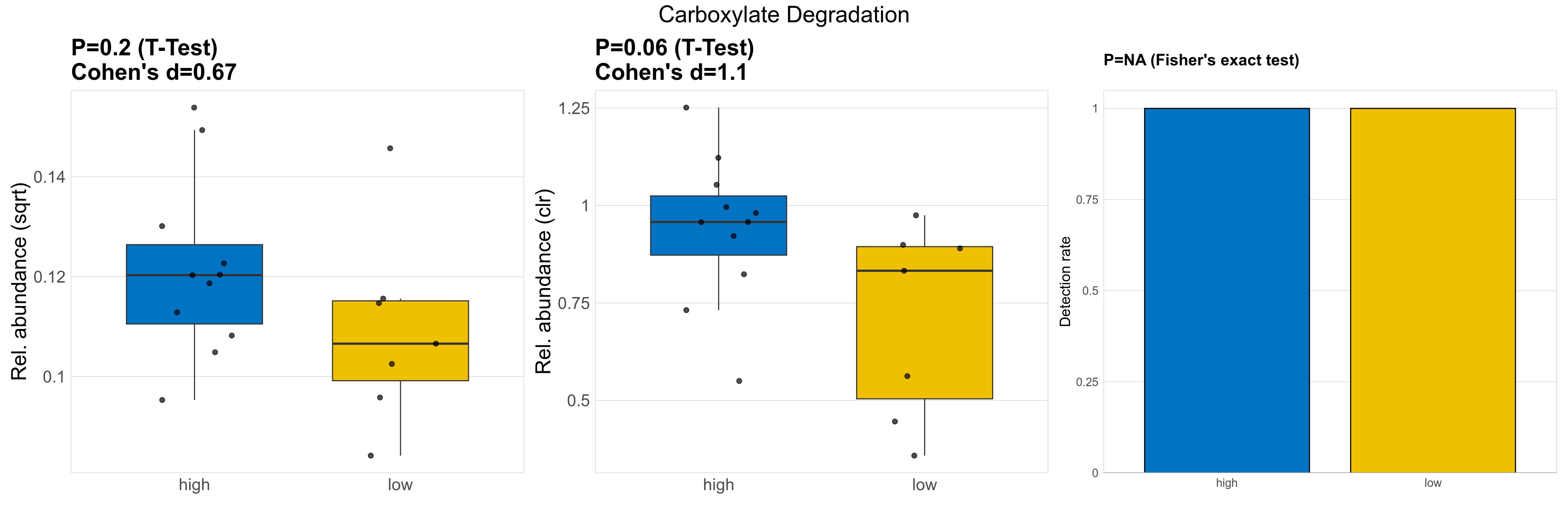
| Carboxylate Degradation | 0.2 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.1 | NA | NA | NA | 0.27 | 0.89 | 0.31 | 0.94 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.0045 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.0045 | -0.32 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| C1 Compound Utilization and Assimilation | 0.42 | 0.78 | 1 | 0.49 | 0.57 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.36 | NA | NA | NA | 0.72 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.071 | 0.069 | 0.072 | 0.0084 | 0.063 | 0.071 | 0.018 | -0.13 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Nucleic Acid Processing | 0.86 | 0.9 | 1 | -0.081 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1 | -0.0091 | NA | NA | NA | 0.71 | 0.95 | 0.66 | 0.98 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.0022 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.0016 | 0 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
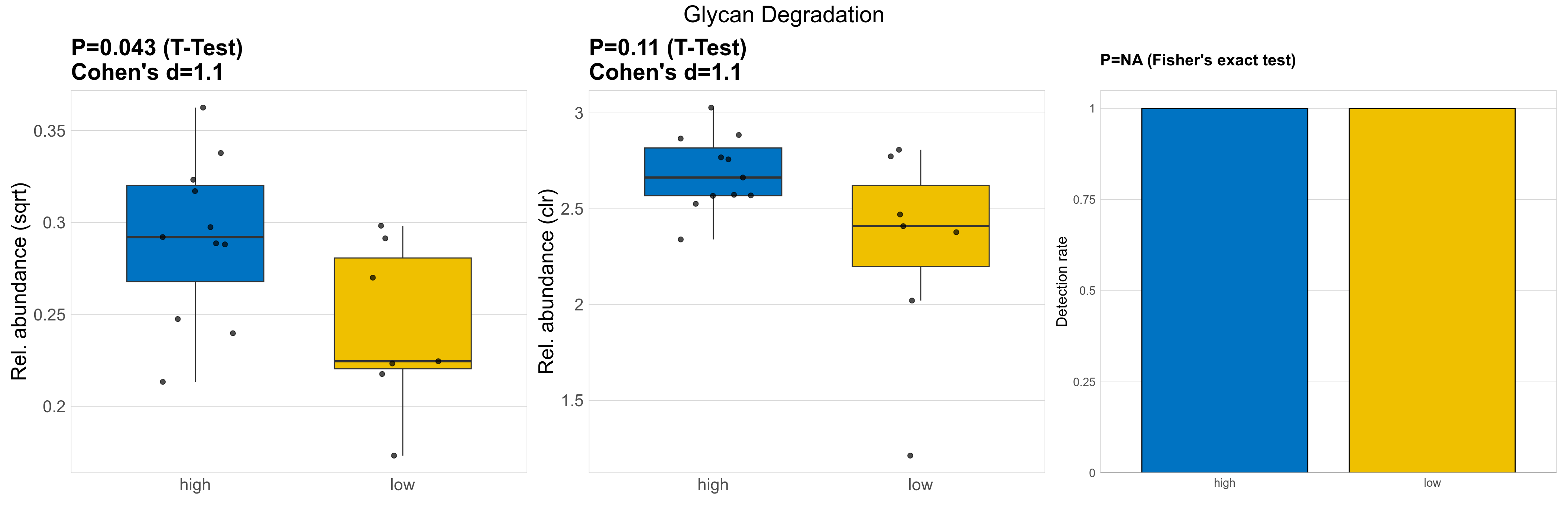
| Glycan Degradation | 0.043 | 0.74 | 1 | 1.1 | 0.11 | 0.9 | 1 | 1.1 | NA | NA | NA | 0.11 | 0.89 | 0.12 | 0.92 | 0.077 | 0.077 | 0.083 | 0.087 | 0.085 | 0.025 | 0.061 | 0.05 | 0.022 | -0.51 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
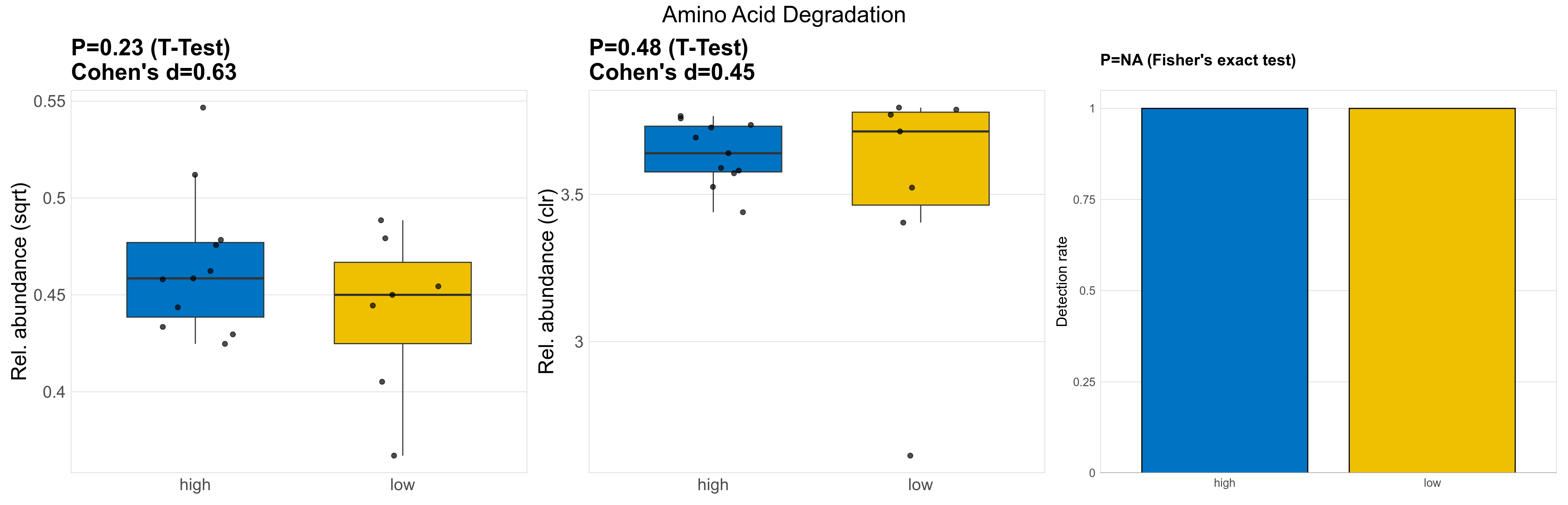
| Amino Acid Degradation | 0.23 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.63 | 0.48 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.45 | NA | NA | NA | 0.65 | 0.9 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.036 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.036 | -0.14 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Fatty Acid and Lipid Degradation | 0.57 | 0.85 | 1 | -0.35 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 1 | 0.057 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 1 | 0.76 | 0.94 | 0.49 | 0.97 | 0.002 | 0.0019 | 0.0013 | 0.0014 | 0.0011 | 0.00085 | 0.0027 | 0.0013 | 0.0036 | 0.95 | 17 / 18 (94%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 6 / 7 (86%) | 1 | 0.857 |
| Respiration | 0.4 | 0.78 | 1 | -0.5 | 0.43 | 0.9 | 1 | -0.4 | 0.64 | 1 | 1 | 0.42 | 0.91 | 0.47 | 0.97 | 0.0014 | 0.00088 | 0.00027 | 0.00047 | 0.00029 | 0.00059 | 0.0015 | 0.00024 | 0.0028 | 1.7 | 11 / 18 (61%) | 6 / 11 (55%) | 5 / 7 (71%) | 0.545 | 0.714 |
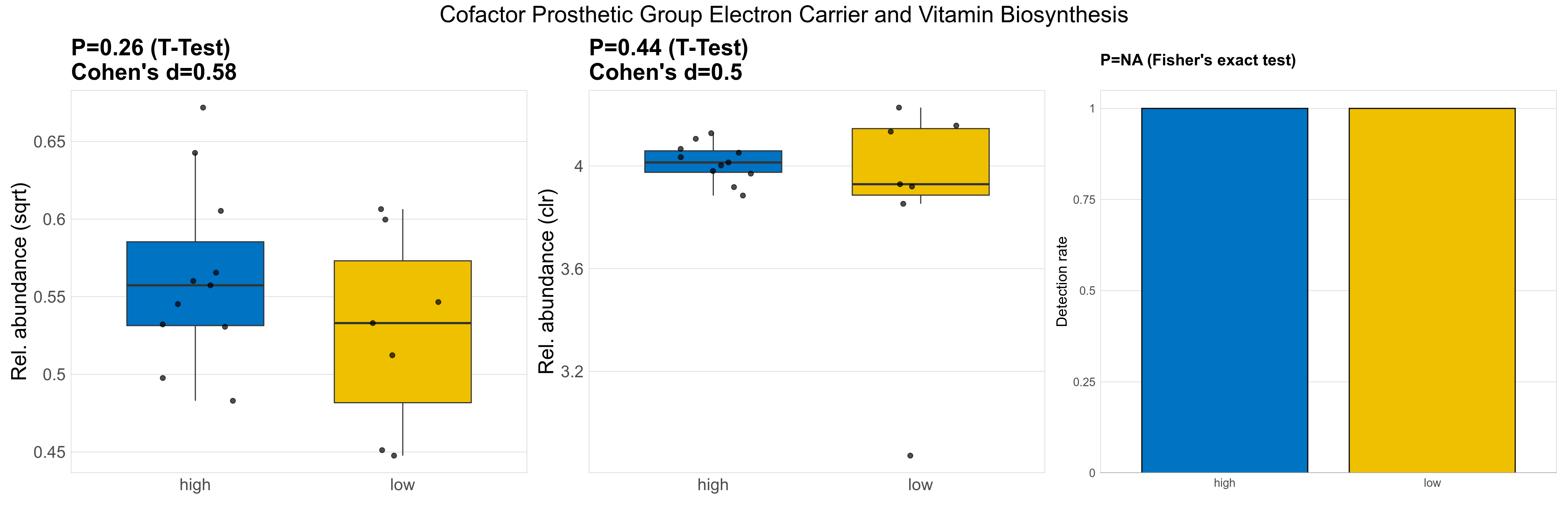
| Cofactor Prosthetic Group Electron Carrier and Vitamin Biosynthesis | 0.26 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.5 | NA | NA | NA | 0.59 | 0.9 | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.3 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.067 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.067 | -0.19 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
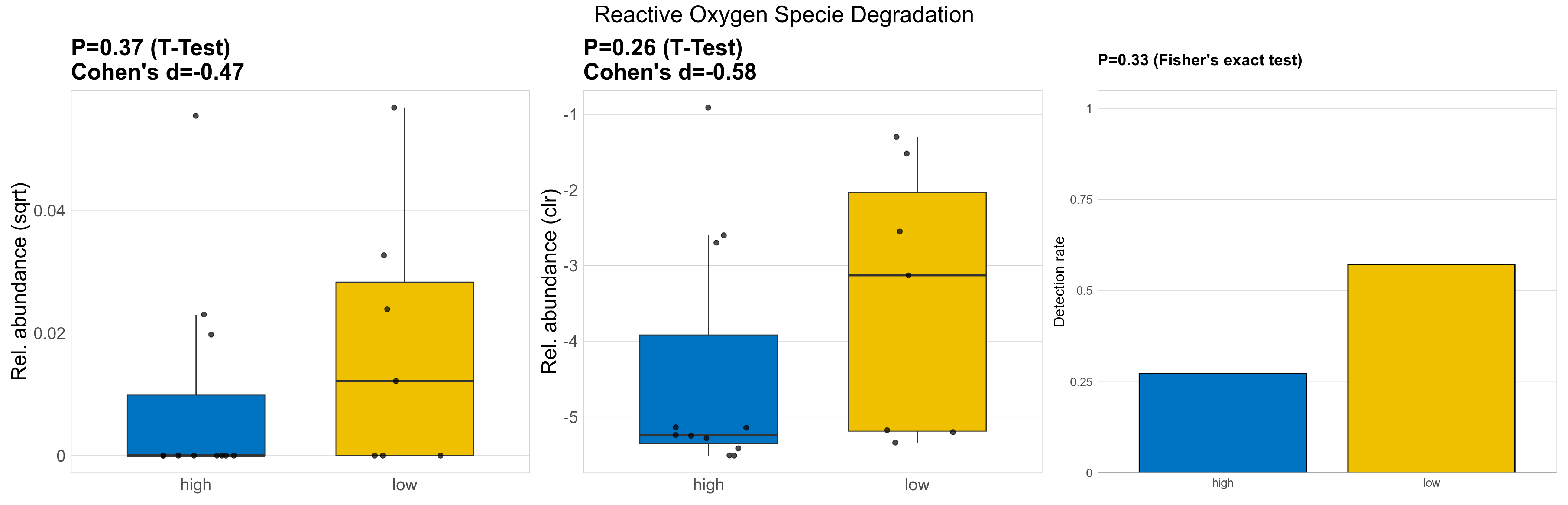
| Reactive Oxygen Specie Degradation | 0.37 | 0.78 | 1 | -0.47 | 0.26 | 0.9 | 1 | -0.58 | 0.33 | 0.87 | 1 | 0.27 | 0.88 | 0.29 | 0.95 | 0.0013 | 5e-04 | 0 | 0.00036 | 0 | 0.00092 | 0.00072 | 0.00015 | 0.0012 | 1 | 7 / 18 (39%) | 3 / 11 (27%) | 4 / 7 (57%) | 0.273 | 0.571 |
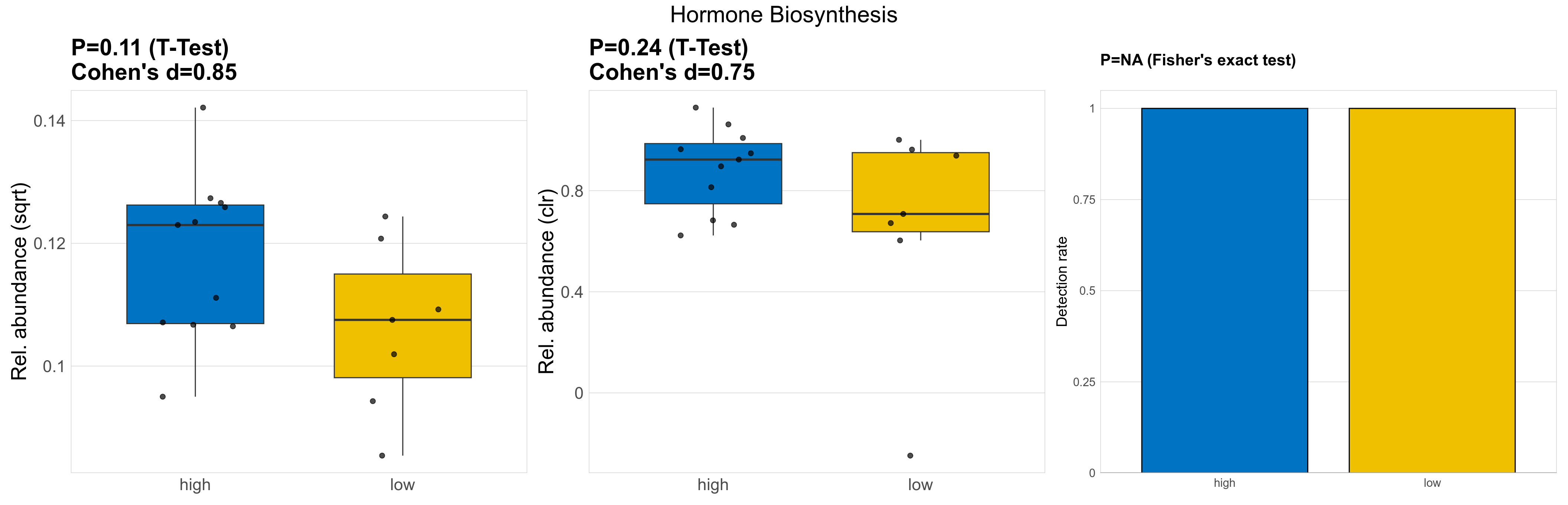
| Hormone Biosynthesis | 0.11 | 0.74 | 1 | 0.85 | 0.24 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.75 | NA | NA | NA | 0.36 | 0.9 | 0.47 | 0.96 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.0032 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.0029 | -0.35 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Nucleoside and Nucleotide Degradation | 0.7 | 0.86 | 1 | -0.23 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 1 | -0.061 | NA | NA | NA | 0.66 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 0.98 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.05 | 0.046 | 0.045 | 0.01 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.021 | 0.15 | 18 / 18 (100%) | 11 / 11 (100%) | 7 / 7 (100%) | 1 | 1 |
| Degradation/Utilization/Assimilation - Other | 0.64 | 0.86 | 1 | -0.23 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 1 | -0.22 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.97 | 0.00037 | 0.00025 | 0.00014 | 0.00022 | 0.00014 | 3e-04 | 0.00029 | 0.00024 | 0.00033 | 0.4 | 12 / 18 (67%) | 7 / 11 (64%) | 5 / 7 (71%) | 0.636 | 0.714 |
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
Click here to open full-sized image in new window.
P Fisher's exact test: differences in detection rate were detected by Fisher's exact test.
P Welch's t-test (sqrt): Differentially abundant functions were identified by Welch's t-test.
P Welch's t-test (clr): Differentially abundant functions were identified by Welch's t-test.
The following plots present the distribution of the top most differentially abundant microbial functions across all applied statistical analysis. Plots are ordered alphabetically.